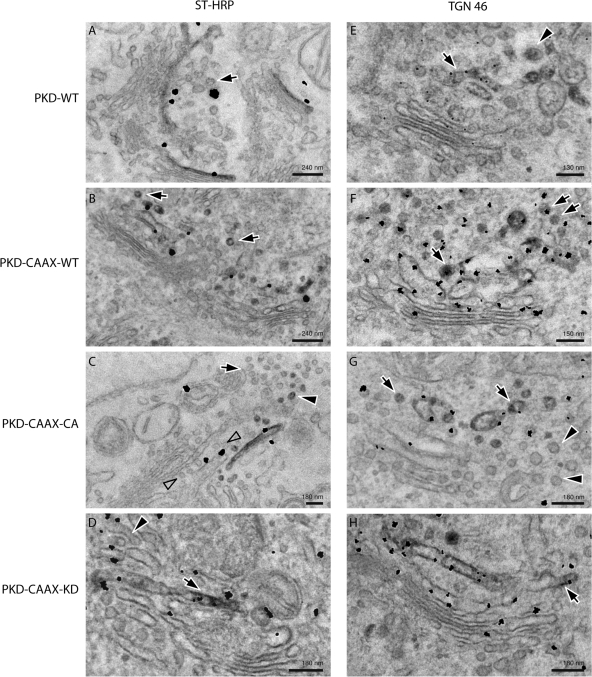
Figure 5.
Analysis of HeLa cells transfected with PKD CAAX isoforms by electron microscopy. HeLa cells transfected with PKD-WT, PKD-CAAX-WT, PKD-CAAX-CA, or PKD-CAAX-KD alone (right) or with ST-HRP (left) were processed for electron microscopy. (A) Gold particles indicating the presence of PKD-WT reveal its presence at the TGN (where ST-HRP is also visible). Few vesicles lacking ST-HRP were also visible in sections (arrow). (B) Expression of PKD-CAAX-WT increased the number of ST-HRP–positive vesicles (arrows). (C) PKD-CAAX-CA induced an increase in the number of vesicles with ST-HRP (arrowheads); however, number of unlabeled vesicles also increases (arrows). Row of vesicles (empty arrows) between ST-positive cisterna and the rest of the stack may represent cisterna consumed by vesicles, and this also might explain why ST-positive cisterna appears to be peeling off. (D) Cells expressing PKD-CAAX-KD exhibit regular trans-Golgi cisterna (arrow) labeled with ST-HRP. Some tubular structures (presumably TGN) are also visible at the trans-face of the Golgi (arrowhead). (E) Cells expressing PKD-WT exhibit regular TGN with both tubular (arrow) and vesicles (arrowhead). PKD is detected at the TGN46-positive membranes. (F) PKD-CAAX-WT induced an increase in the number of TGN46-positive vesicles (arrows). (G) Expression of PKD-CAAX-CA induced extensive vesiculation of the Golgi apparatus. Both TGN46-positive (arrows) and TGN46-negative (arrowheads) vesicles increased in numbers under these conditions. PKD is detected at the TGN46-positive membranes. (H) Long TGN46-positive (arrows) tubular structures were detected in PKD-CAAX-KD–expressing cells without any obvious increase in number of vesicles.