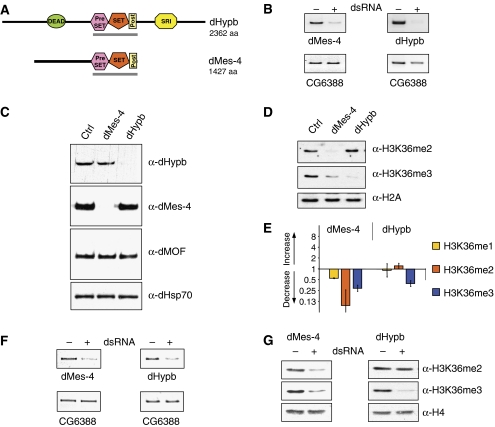
Figure 3.
Identification of Drosophila SET domain proteins involved in H3K36 methylation. (A) Domain structure of full-length HMTase proteins as predicted by the SMART software (EMBL). DEAD=ATP dependant helicase domain, SRI=Set2 Rpb1 interacting domain. The gray bar indicates protein fragments tested for HMTase activity in vitro. (B) Validation of mRNA knockdown in cultured Kc cells. RT–PCR of target message in the absence (−) or presence (+) of dsRNA reveals efficient mRNA knockdown. The gene expression of CG6388 is unaffected in both knockdowns and serves as a loading control. (C) Validation of protein reduction. Western blot using antibodies specific for dMes-4 and dHypb in the absence (−) or presence (+) of dsRNA reveals efficient reduction of the targeted proteins in Kc cells. dHsp70 and dMOF are unaffected by RNAi knockdown and serve as loading control. (D) Reductions of dMes-4 and dHypb have specific effects on global levels of H3K36 methylation. Loss of dHypb results in the reduction of H3K36me3 and coinciding increase of H3K36me2. Knockdown of dMes-4 leads to a reduction in both H3K36me2 and H3K36me3. H2A serves as loading control. Global levels of H3 and H4 were unaffected (Supplementary Figure 5A). (E) Mass spectrometry analysis of H3K36-methylated peptides. MS-MS analysis of mono-, di- or trimethylated H3K36 moieties following knockdown of putative HMTases in Drosophila Kc cells. The bar chart displays fold changes in the abundance of H3K36 methylation states relative to untreated control cells. (F) Knockdown of putative Drosophila H3K36 HMTases in vivo. RT–PCR from larvae uninduced (−) or induced (+) for targeted knockdown of either dMes-4 or dHypb mRNA in vivo. Reduced transcript abundance is detected in the presence of GAL4 driver under the control of a ubiquitously expressed (tubulin) promoter. CG6388 mRNA levels serve as loading control. (G) Western blot analysis of H3K36 methylation states in fly larvae mirror the observations in cultured cells. Reduction of dMes-4 message results in the reduction of H3K36 di- and trimethylation, whereas dHypb RNAi specifically downregulates H3K36me3. Levels of total H4 serve as loading control.