Figure 3.
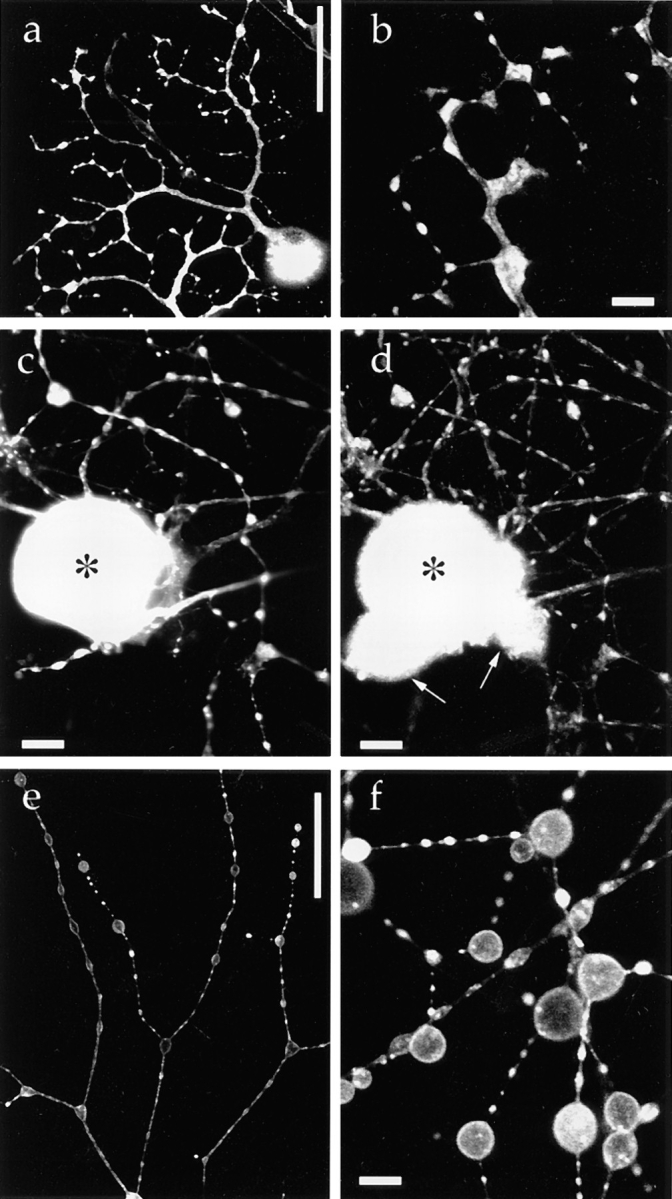
Targeting of a synaptic vesicle protein–GFP fusion protein in mouse DRG neurons. 40 h after infection with adenovirus vector carrying synaptophysin–GFP chimeric DNA, living cells were examined using confocal laser scan microscopy unless otherwise indicated. (a) Low magnification. Synaptophysin–GFP is accumulated in varicosities. (b) Confocal slice observed at higher magnification revealed that synaptophysin–GFP is localized in the cytoplasm in varicosities. (c and d) Double labeling of fixed DRG cells with synaptophysin–GFP (c) and endogenous synaptic vesicle protein SV2 (d). In the clump of cell bodies, only the cell indicated by (*) expressed synaptophysin–GFP, whereas the other cell bodies (arrows) were not labeled by GFP. Axons and cell bodies that expressed synaptophysin–GFP exhibited the colocalization of synaptophysin–GFP and SV2. (e and f) Synaptophysin–GFP was exocytosed onto the plasma membrane after stimulation with 3 nM latrotoxin and EGTA. Synaptophysin– GFP redistributed in the plasma membrane of varicosities. Because synaptic vesicles were fused with the plasma membrane, the total surface area of the varicosities was markedly increased. Bars: (a and e) 50 μm; (c and d) 10 μm; (b and f) 5 μm.
