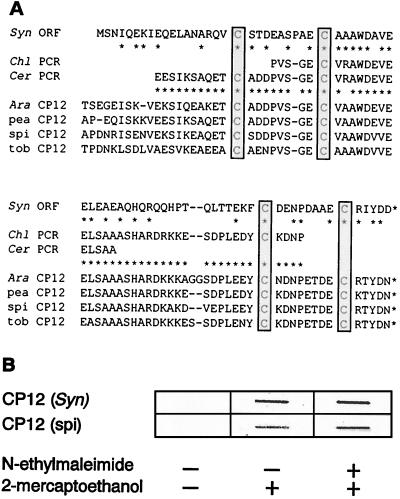
Figure 1.
CP12 is an evolutionarily conserved protein of photosynthetic organisms. (A) Known primary structures of CP12 proteins of higher plants, derived from cDNA translations, were aligned with the translation of an ORF in the genomic DNA sequence of Synechocystis (strain PCC6803) and cloned PCR products out of cDNA libraries, made from RNA of C. reinhardtii (unpublished) and Ce. purpureus. Conserved cysteine residues are boxed. Amino acid residues of the Synechocystis CP12 as well as of Chlamydomonas and Ceratodon PCR product translations, which are identical with at least one residue of the higher plant CP12 peptides, are marked by asterisks. (B) The conserved cysteine residues of CP12 form peptide loops via disulfide bonds. Equal amounts of His-tagged Synechocystis and spinach CP12, overexpressed in E. coli and purified by metal ion affinity, were slot blotted onto nitrocellulose. The filters were treated with alkylating and/or reducing reagents and subsequently analyzed for the presence of reduced thiol groups by a colorimetric assay following the protocol for the DIG Protein Detection Kit (Boehringer Mannheim).