Fig.1.
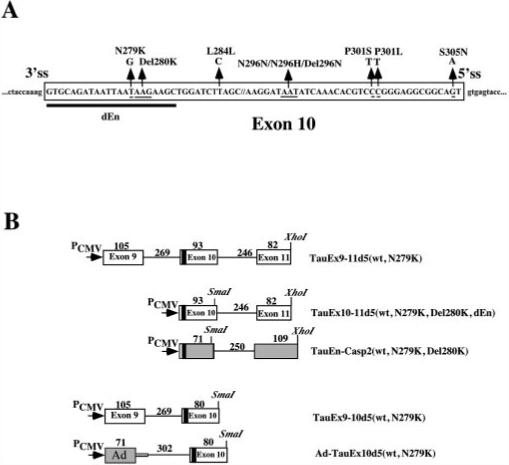
A, positions of reported mutations in exon 10 of the human tau gene. 5′ss, 5′ splice site. 3′ss, 3′ splice site. The sequence deleted from TauEx10−11d5(WT) to generate TauEx10−11d5(dEn) is indicated by the thick black line. B, schematics of a series of tau minigene constructs. The genomic DNA fragments containing exons 9, 10 (WT, N279K, Del280K, and dEn), and 11 as well as intronic sequences flanking exon 10 were inserted in mammalian expression vector pcDNA3 under the control of the cytomegalovirus promoter (PCMV). The AG-rich region in exon 10 is indicated by the black box. The caspase-2 (casp2) exon 9 and 10 splicing unit and first exon region (L1) of the Ad major late transcription unit are shown in gray boxes. The sizes of the corresponding exons and introns are indicated above the respective regions (in base pairs).
