Fig.3. Exonic mutations in the AG-rich region of exon 10 affect the splicing with both upstream and downstream exons.
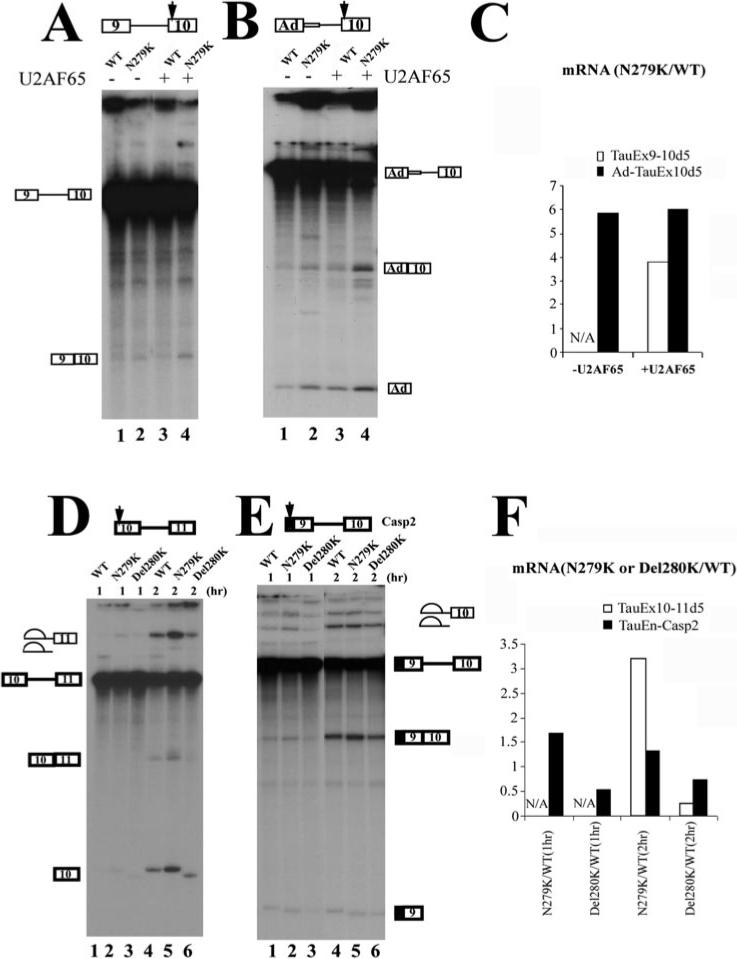
The position of the AG-rich element in each construct is indicated by the arrow. Shown in the figures are in vitro splicing reaction products using pre-mRNA transcripts derived from TauEx9−10 (A), Ad-TauEx10 (B), TauEx10−11 (D), or TauEn-Casp2Ex9−10 (E) plasmids. In A and B, the AG-rich enhancer with WT sequence or N279K mutation is located in the downstream exon. In D and E, the AG-rich element with WT, N279K, or Del280K is located in the upstream exon. The quantification was performed using a PhosphorImager and is expressed as the ratio of corresponding splicing products (ligated exons) produced in the reactions containing either WT or mutant pre-mRNA substrates. N/A, reactions with splicing products below the detection level. The N279K point mutation increases the efficiency of the splicing with both upstream and downstream exons. Del280K reduces the splicing efficiency, as indicated by the quantification shown in C and F.
