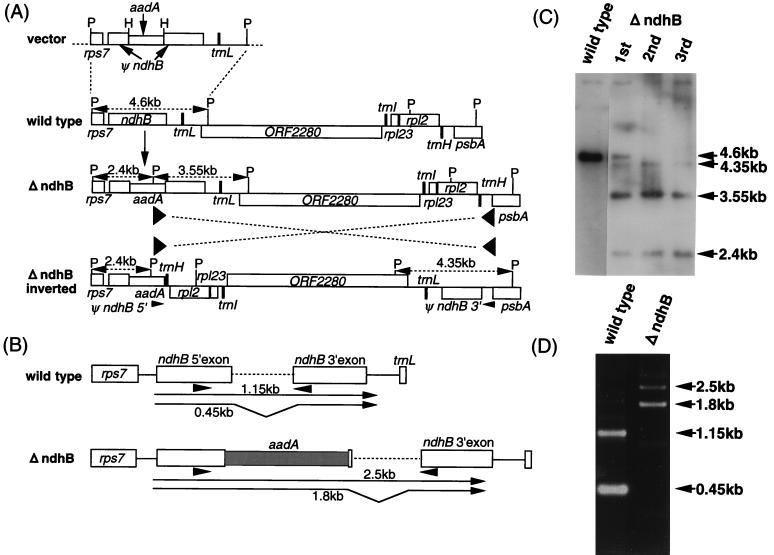
Figure 1.
Gene disruption of ndhB by plastid transformation. (A) The 5′ exon of ndhB was disrupted by insertion of the aadA cassette at the unique HindIII site (vector). Disrupted ndhB (ψndhB) was incorporated into the wild-type genome by two homologous recombination events (ΔndhB). The PstI fragment sizes detected by Southern hybridization are shown. Sequence inversion occurred via the duplicated psbA terminator sequences indicated by the arrowheads (ΔndhB inverted). HindIII and PstI sites are indicated by H and P, respectively. (B) Schematic representation of the transcripts in wild-type and ΔndhB tobacco chloroplasts. Arrowheads indicate the positions of the PCR primers. Reverse transcription–PCR fragment sizes are indicated. (C) Total cellular DNA extracted from the wild-type and transformed tobacco plants after the first, second, and third rounds of spectinomycin selection was digested with PstI, then analyzed by Southern hybridization with a 4.6-kb PstI fragment as the probe. (D) Total cellular RNAs extracted from wild-type and ΔndhB plants were used to synthesize cDNA. For reverse transcription–PCR, the primers used are as indicated in B.