Figure 3. TFII-I isoforms may connect lipid metabolism to gene expression.
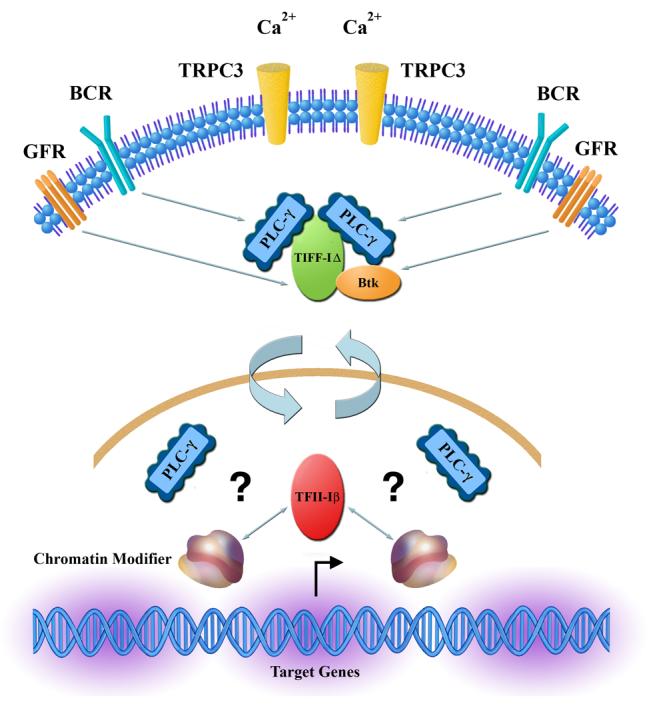
Because both isoforms of TFII-I have been described to interact with PLC-γ, we propose that TFII-IΔ interacts with (soluble) PLC-γ in the cytoplasm to regulate TRPC-3 mediated Ca2+ entry, while TFII-Iβ interacts with PLC-γ in the nucleus. In addition, TFII-I also interacts with Btk in the cytoplasm. Because TFII-Iβ interacts with chromatin modifiers such as HDACs and LSD1 and PLC-γ has been shown to play a role in transcription, it is possible that TFII-Iβ might connect phopsholipid metabolism to signal-induced gene regulation. Given the signal-induced reverse translocation of TFII-I isoforms, such a process might also lead to alteration in subcellular PLC-γ.
