Figure 6.
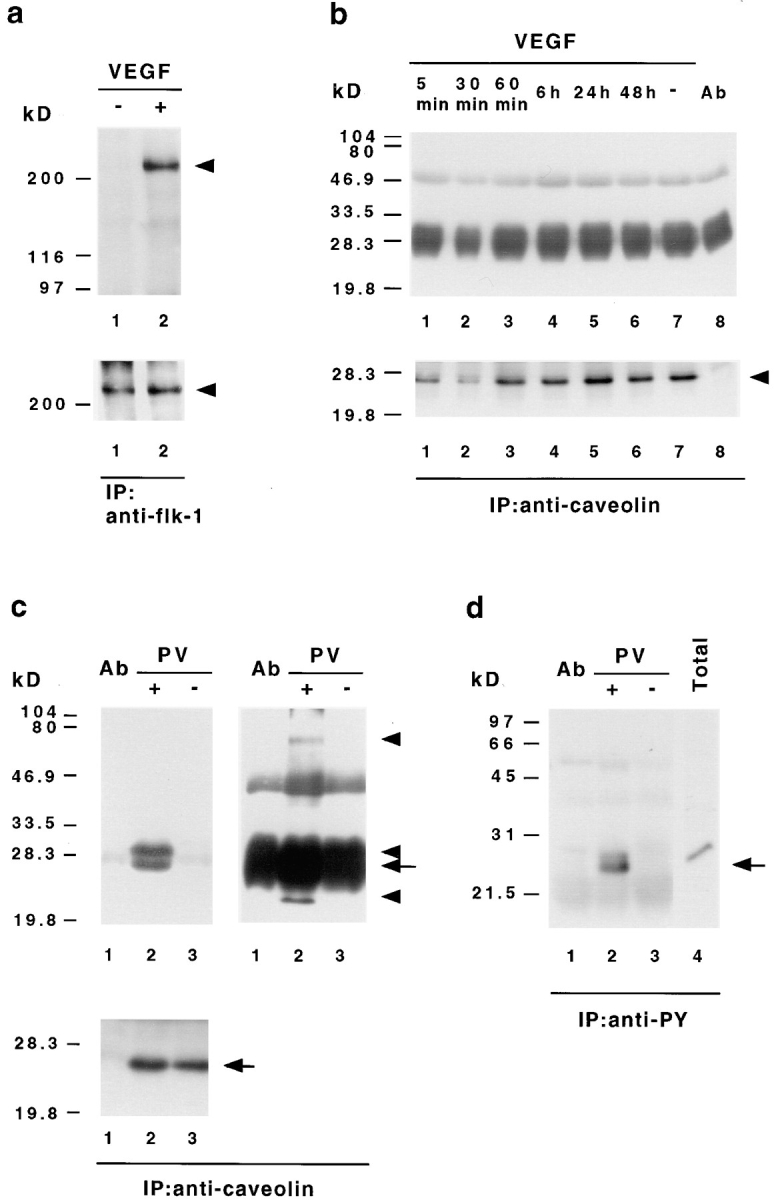
VEGF-induced signal transduction does not stimulate tyrosine phosphorylation of caveolin-1. (a) Tyrosine phosphorylation of bovine VEGF receptor-2 (flk-1) in ACE cells after VEGF stimulation. Endothelial cells were stimulated with (+) or without (−)100 ng/ml VEGF 165 for 5 min, extracted with Triton buffer, and then immunoprecipitated with anti–flk-1 antibodies. The precipitates were analyzed by Western immunoblotting with an antibody against phosphotyrosine (top). The same membrane was afterwards reprobed with an antibody recognizing flk-1 (bottom). In contrast to unstimulated cells (lane 1) bovine flk-1 (arrowhead) is found to be specifically phosphorylated on tyrosine after VEGF treatment (lane 2). (b) VEGF does not induce caveolin-1 tyrosine phosphorylation. ACE cells grown on basal lamina-type extracellular matrix were stimulated with VEGF 165 for the indicated time, extracted with SDS lysis buffer, immunoprecipitated with VIP-21N antibody, and then subjected to immunoblot analysis with antiphosphotyrosine antibody (top). Subsequent reprobing of the same membrane with anti–caveolin-1 antibody (bottom) indicated that equal amounts of caveolin-1 (arrowhead) have been precipitated. Protein bands at 50 and 30–25 kD corresponding to the IgG heavy and light chains eluted from the Sepharose, together with the bound proteins, are also present in immunoprecipitations without cell lysates (top, lane 8). (c and d) Pervanadate-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of caveolin-1 and associated proteins. ACE cells were treated with (+) or without (−) pervanadate (PV), extracted with SDS lysis buffer, and then subjected to immunoprecipitation with antibodies against caveolin-1 (c) or phosphotyrosine (d), followed by Western immunoblotting with antiphosphotyrosine (c, top) or anticaveolin-1 (d) antibodies. Blots of caveolin-1 immunoprecipitates were reprobed with anti–caveolin-1 antibody (c, bottom). The bands at 50 and 30–25 kD correspond to the IgG heavy and light chains. To reveal all precipitated phosphoproteins, two different exposures for the antiphosphotyrosine blots are shown in c. Note that the anticaveolin-1 antibody detects only one band in antiphosphotyrosine- and anti–caveolin-1 precipitates (c and d, arrows), whereas the antiphosphotyrosine antibody recognizes several proteins in the anticaveolin-1 precipitates (c, top arrowheads). As controls, immunoprecipitations without cell lysates (lanes 1 in c and d) and total cellular extracts (d, lane 4) are shown.
