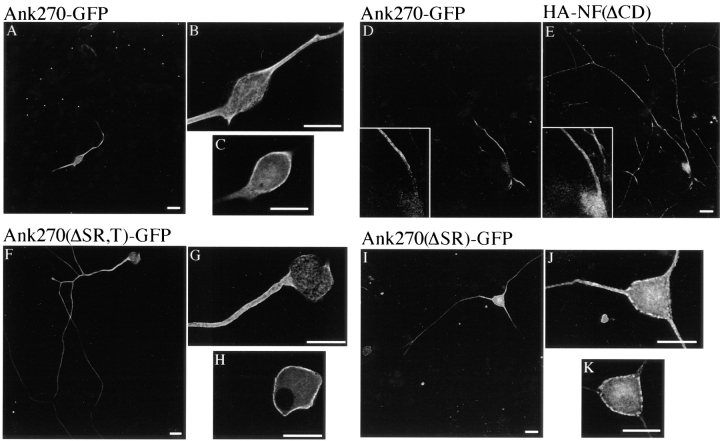
Figure 3.
The unique serine-rich and tail domain of ankyrinG contribute to restriction of 270-kD ankyrinG at the axon proximal segment. The cDNAs of 270-kD ankyrinG and its variants lacking the serine-rich and/or tail domains are transfected into 8-d-old DRG culture using Helios™ Gene Gun system. Expression of transfected proteins is visualized by immunostaining of the GFP tag. The transfected 270-kD ankyrinG (Ank270-GFP) is highly restricted to the proximal segment (A). High zoom recording reveals plasma membrane stain of the transfected 270-kD ankyrinG at the proximal segment (B) and the cell body (C). The restricted location of transfected Ank270–GFP (D) is displayed against the full length of the transfected axon which is revealed by double labeling of the cotransfected cytoplasmic domain-deleted neurofascin (E). The transfected 190-kD ankyrin (Ank270[ΔSR,T]–GFP) is also localized at the plasma membrane of the proximal segment (G) and the cell body (H). However, a significant amount of the transfected Ank270(ΔSR,T)–GFP is distributed beyond the proximal segment into the axon (F). Insertion of the tail domain into Ank270(ΔSR,T)– GFP (Ank270[ΔSR]–GFP) improves but does not totally restore restriction of the transfected ankyrin to the proximal part of the axon (I). J and K show membrane localization of Ank270(ΔSR)–GFP at the proximal segment and the cell body respectively. Bar, 25 μm.