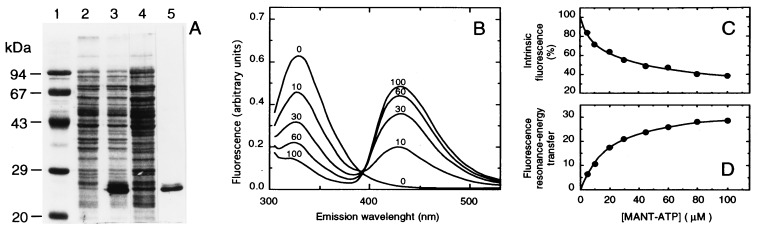
Figure 1.
Purification of the H6-NBD2 recombinant domain and interaction with MANT-ATP. (A) Fractions obtained from a 1-liter culture of E. coli cells overexpressing the cDNA encoding H6-NBD2 were analyzed by SDS/PAGE. Lanes: 1, molecular mass markers corresponding to phosphorylase b (94 kDa), BSA (67 kDa), ovalbumin (43 kDa), carbonic anhydrase (29 kDa), and soybean trypsin inhibitor (20 kDa); 2, total bacteria proteins before IPTG induction; 3, total bacteria proteins after IPTG induction; 4, soluble proteins from the supernatant; 5, purified domain obtained after nickel-chelate affinity chromatography. (B) Modifications of H6-NBD2 fluorescence spectrum upon interaction with MANT-ATP. The emission fluorescence of 3.2 μM H6-NBD2 was recorded after excitation at 295 nm in 1.2 ml of dialysis buffer (see Experimental Procedures), at pH 6.8, in the presence of increasing MANT-ATP concentrations from 0 to 100 μM, as indicated on each trace and corrected for buffer contribution. The concentration-dependent binding of MANT-ATP was analyzed by progressive quenching of H6-NBD2 intrinsic fluorescence, determined by spectral integration from 310 to 380 nm, and corrected for innerfilter effect (C), and by the increase in fluorescence resonance-energy transfer between tryptophan and bound MANT-ATP, monitored in the range 400–530 nm (D).