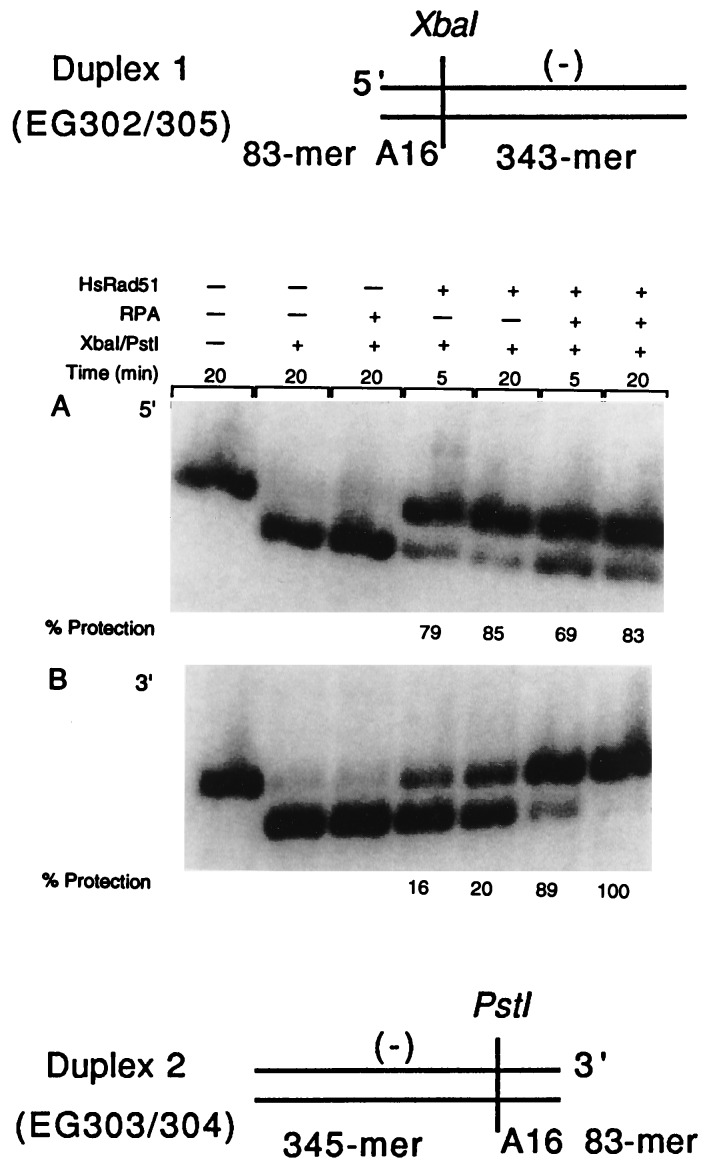
Figure 1.
Formation of homologous joints at either end of duplex DNA in the presence of RPA. For this assay, the presynaptic filament was formed on oligonucleotide A16(−) and the duplex DNAs were duplex 1 (EG302/305) and duplex 2 (EG303/304). Duplexes 1 and 2 possessed AT-rich A16 sequences at the 3′ end or 5′ end of the displaced strand, respectively. Duplex 1 (426-mer), used for the experiment presented in A, tests for pairing at the 5′ end whereas duplex 2, a 428-mer duplex (B) detects pairing at the 3′ end. We monitored protection of the XbaI site resulting from the reaction between A16 and EG302/305 and protection of the PstI site resulting from the reaction between A16 and EG303/304. Restriction enzymes were used in an amount that was sufficient to cleave the substrate DNA in 30 sec in absence of pairing. 32P-labeled 426-mer duplex 1 (lane 1, A) and 428-mer duplex 2 (lane 1, B) were cleaved, respectively, into a 333-mer (lane 2, A) and a 335-mer (lane 2, B) fragment on restriction cleavage. When filaments were formed on a heterologous oligonucleotide, no protection of the restriction sites was observed (data not shown).