Abstract
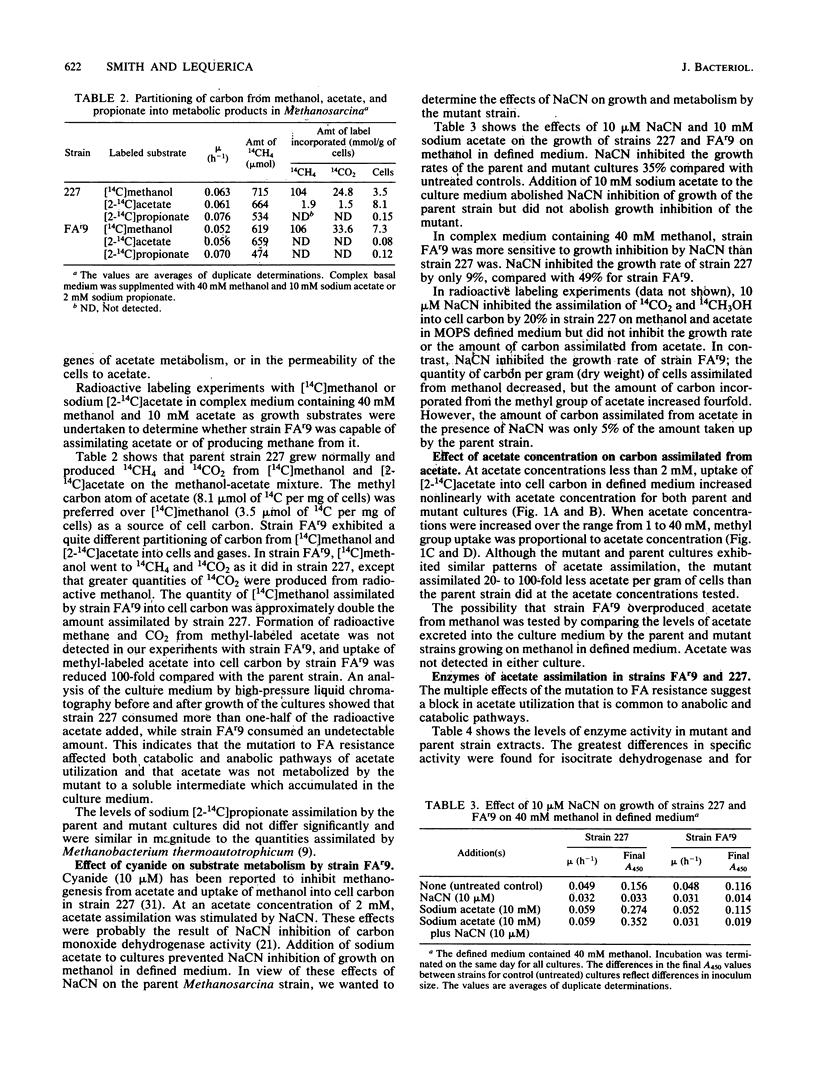
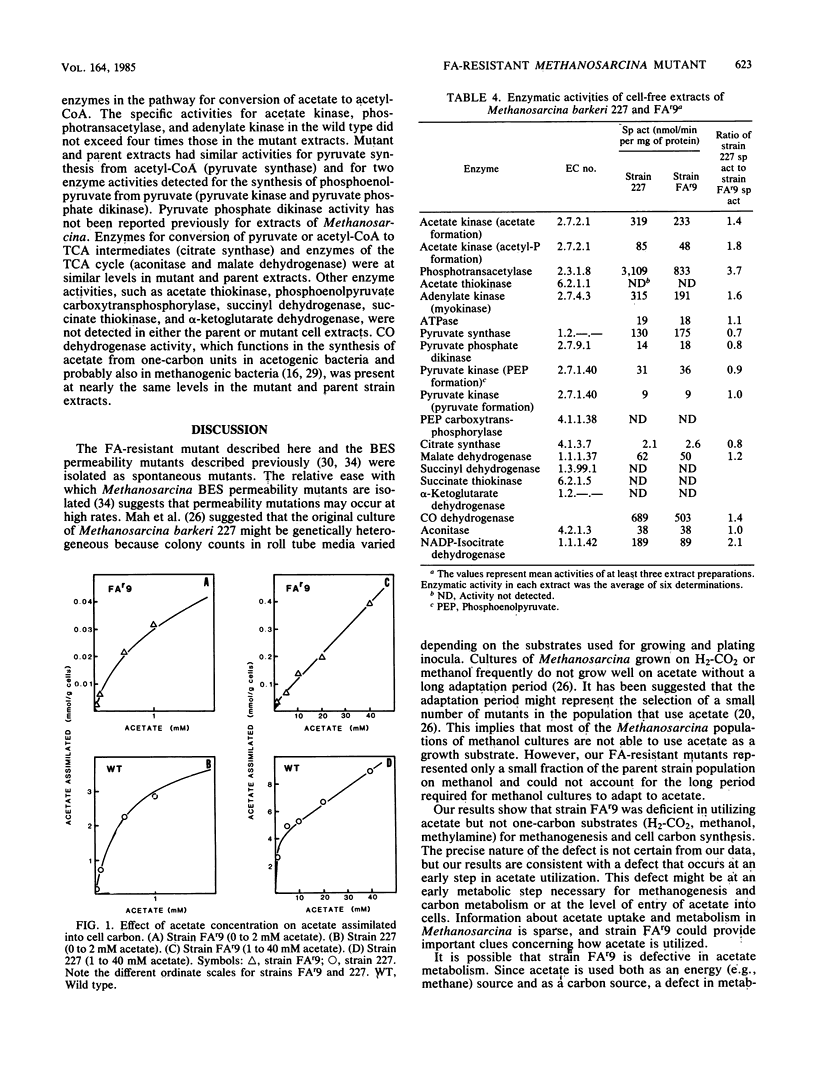
Mutants of Methanosarcina barkeri 227 resistant to monofluoroacetate were isolated from monofluoroacetate-treated cultures. Mutant strain FAr9 was 100 times more resistant to monofluoroacetate than the wild-type strain and was deficient in carbon uptake and CH4 and CO2 production from methyl-labeled acetate. Methanol was assimilated at increased levels. Strain FAr9 was unable to shift from using methanol to using acetate for growth and exhibited increased sensitivity to growth inhibition by NaCN in methanol-containing complex medium. Unlike parent strain 227, acetate addition to methanol-containing media did not prevent NaCN inhibition. The specific activities of enzymes of exogenous acetate assimilation, CO dehydrogenase, and enzymes of the tricarboxylic acid cycle were similar for mutant and parent strain cell extracts. Mutation to monofluoroacetate resistance did not confer simultaneous resistance to 2-bromoethanesulfonate or pyruvate or alter propionate uptake. We conclude that strain FAr9 is either an acetate permeability mutant or is defective in an activation step required for the catabolism and anabolism of acetate.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balch W. E., Fox G. E., Magrum L. J., Woese C. R., Wolfe R. S. Methanogens: reevaluation of a unique biological group. Microbiol Rev. 1979 Jun;43(2):260–296. doi: 10.1128/mr.43.2.260-296.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baresi L. Methanogenic cleavage of acetate by lysates of Methanosarcina barkeri. J Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;160(1):365–370. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.1.365-370.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckler G. S., Hook L. A., Reeve J. N. Chloramphenicol acetyltransferase should not provide methanogens with resistance to chloramphenicol. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Apr;47(4):868–869. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.4.868-869.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels L., Fuchs G., Thauer R. K., Zeikus J. G. Carbon monoxide oxidation by methanogenic bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1977 Oct;132(1):118–126. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.1.118-126.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels L., Sparling R., Sprott G. D. The bioenergetics of methanogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Sep 6;768(2):113–163. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(84)90002-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenealy W. R., Zeikus J. G. One-carbon metabolism in methanogens: evidence for synthesis of a two-carbon cellular intermediate and unification of catabolism and anabolism in Methanosarcina barkeri. J Bacteriol. 1982 Aug;151(2):932–941. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.2.932-941.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenealy W., Zeikus J. G. Influence of corrinoid antagonists on methanogen metabolism. J Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;146(1):133–140. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.1.133-140.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krzycki J. A., Wolkin R. H., Zeikus J. G. Comparison of unitrophic and mixotrophic substrate metabolism by acetate-adapted strain of Methanosarcina barkeri. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jan;149(1):247–254. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.1.247-254.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krzycki J. A., Zeikus J. G. Characterization and purification of carbon monoxide dehydrogenase from Methanosarcina barkeri. J Bacteriol. 1984 Apr;158(1):231–237. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.1.231-237.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovley D. R., White R. H., Ferry J. G. Identification of methyl coenzyme M as an intermediate in methanogenesis from acetate in Methanosarcina spp. J Bacteriol. 1984 Nov;160(2):521–525. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.2.521-525.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mah R. A., Smith M. R., Baresi L. Studies on an acetate-fermenting strain of Methanosarcina. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Jun;35(6):1174–1184. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.6.1174-1184.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson M. J., Ferry J. G. Carbon monoxide-dependent methyl coenzyme M methylreductase in acetotrophic Methosarcina spp. J Bacteriol. 1984 Nov;160(2):526–532. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.2.526-532.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberlies G., Fuchs G., Thauer R. K. Acetate thiokinase and the assimilation of acetate in methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. Arch Microbiol. 1980 Dec;128(2):248–252. doi: 10.1007/BF00406167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pezacka E., Wood H. G. The synthesis of acetyl-CoA by Clostridium thermoaceticum from carbon dioxide, hydrogen, coenzyme A and methyltetrahydrofolate. Arch Microbiol. 1984 Jan;137(1):63–69. doi: 10.1007/BF00425809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. R., Lequerica J. L., Hart M. R. Inhibition of methanogenesis and carbon metabolism in Methanosarcina sp. by cyanide. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):67–71. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.67-71.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. R., Mah R. A. Acetate as sole carbon and energy source for growth of methanosarcina strain 227. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 May;39(5):993–999. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.5.993-999.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. R., Mah R. A. Growth and methanogenesis by Methanosarcina strain 227 on acetate and methanol. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Dec;36(6):870–879. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.6.870-879.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. R. Reversal of 2-bromoethanesulfonate inhibition of methanogenesis in Methanosarcina sp. J Bacteriol. 1983 Nov;156(2):516–523. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.2.516-523.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sowers K. R., Baron S. F., Ferry J. G. Methanosarcina acetivorans sp. nov., an Acetotrophic Methane-Producing Bacterium Isolated from Marine Sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 May;47(5):971–978. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.5.971-978.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thauer R. K., Jungermann K., Decker K. Energy conservation in chemotrophic anaerobic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Mar;41(1):100–180. doi: 10.1128/br.41.1.100-180.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weimer P. J., Zeikus J. G. Acetate assimilation pathway of Methanosarcina barkeri. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):332–339. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.332-339.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeikus J. G., Fuchs G., Kenealy W., Thauer R. K. Oxidoreductases involved in cell carbon synthesis of Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. J Bacteriol. 1977 Nov;132(2):604–613. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.2.604-613.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeikus J. G., Kerby R., Krzycki J. A. Single-carbon chemistry of acetogenic and methanogenic bacteria. Science. 1985 Mar 8;227(4691):1167–1173. doi: 10.1126/science.3919443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeikus J. G. The biology of methanogenic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Jun;41(2):514–541. doi: 10.1128/br.41.2.514-541.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


