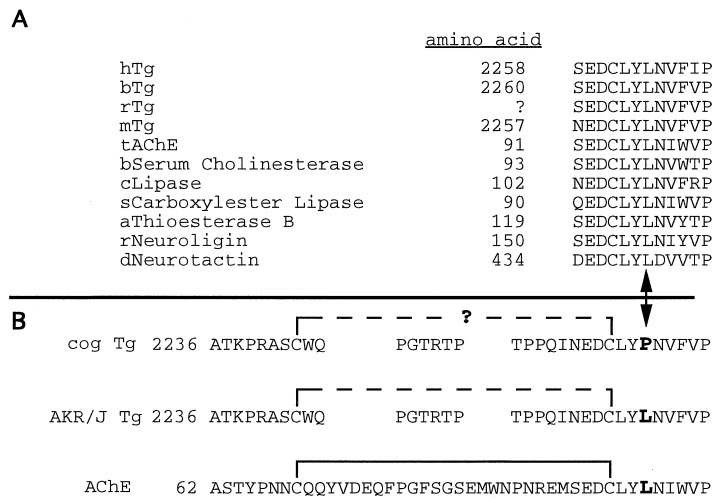
Figure 2.
The cog mutation is located within a conserved structural domain. (A) The amino acids surrounding Leu-2263 (denoted with an arrowhead, at bottom) are highly conserved in Tg from all four species that have thus far been examined, as well as in AChE and other members of the “α/β hydrolase fold” family (a partial list is shown; h, human; b, bovine; r, rat; m, mouse; t, torpedo; c, candida; s, salmon; a, avian; d, Drosophila). The amino acid numbering for rat Tg is not established because the cDNA sequence has not yet been determined in its entirety. (B) Given the close proximity of Leu-2263 to Cys-2260, which forms an intrachain disulfide bond (solid bracket) that provides important structural stability to AChE (see text) and is likely to play a similar role in Tg (dashed bracket), we hypothesize that the cog mutation (L2263P) may destabilize this region, potentially by preventing proper formation of this disulfide bridge (signified by question mark).