Fig. 5. ATP hydrolytic activity in preparations of PDK2.
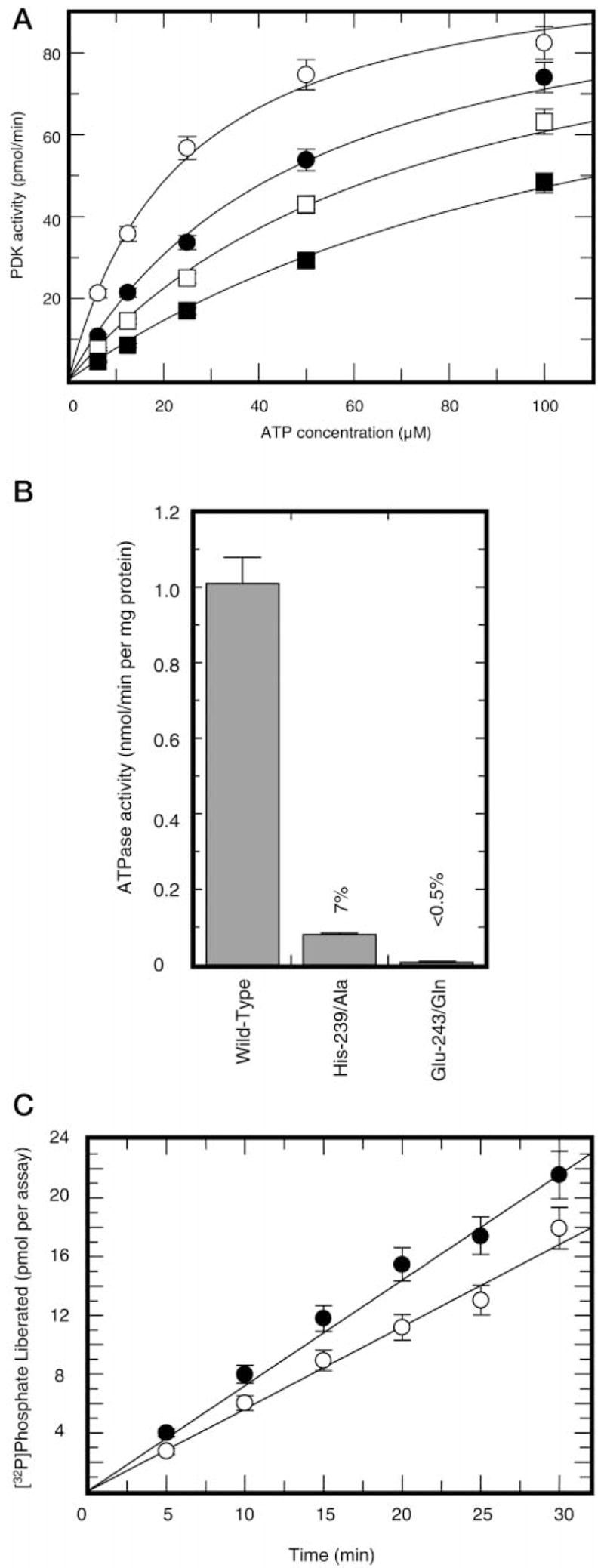
Panel A, inhibition of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase activity by radicicol. Kinase activity was determined without radicicol (○) or in the presence of radicicol at concentrations of 25 μM (●), 50 μM (■), or 100 μM (□). Panel B, radicicol-sensitive ATP hydrolytic activity in preparations of wild-type, Glu-243 → Gln, and His-239 → Ala PDK2. Total ATP hydrolysis was measured in the absence of radicicol with 10 μM [γ-32P]ATP as a substrate. Nonspecific hydrolysis was determined in the presence of 200 μM radicicol. Shown is radicicol-sensitive ATPase activity (difference between total and nonspecific activity) intrinsic to PDK2. Panel C, radicicol-sensitive (○) versus E1-sensitive (●) ATPase activity in preparations of wild-type PDK2. Radicicol-sensitive ATPase activity was determined essentially as described in the legend to panel B. E1-sensitive ATPase activity was determined as a difference between total ATPase activity and ATPase activity measured in the presence of E1 component (final concentration 1.0 mg/ml).
