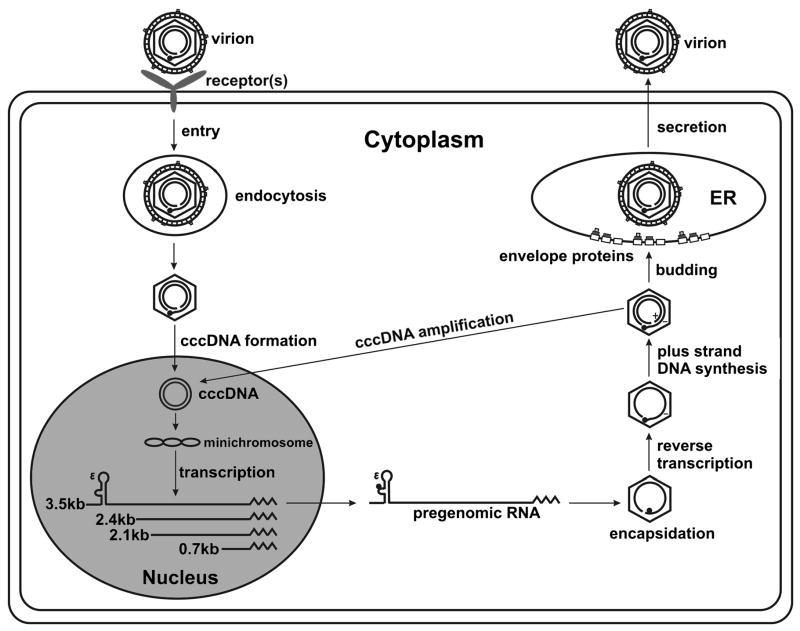
Figure 2. A schematic outline of the HBV replication cycle.
Major steps in the molecular biology of the HBV replication life cycle are shown, from attachment to translocation of the virion DNA to the nucleus, to conversion of entering viral DNA into cccDNA, followed by transcription of the cccDNA into the viral RNA gene products. Encapsidations in the cytoplasm, virion morphogenesis and secretion is also shown. Note, replicated progeny HBV DNA can return to the nucleus by way of an intracellular pathway, which may result in an “auto” amplification of cccDNA.