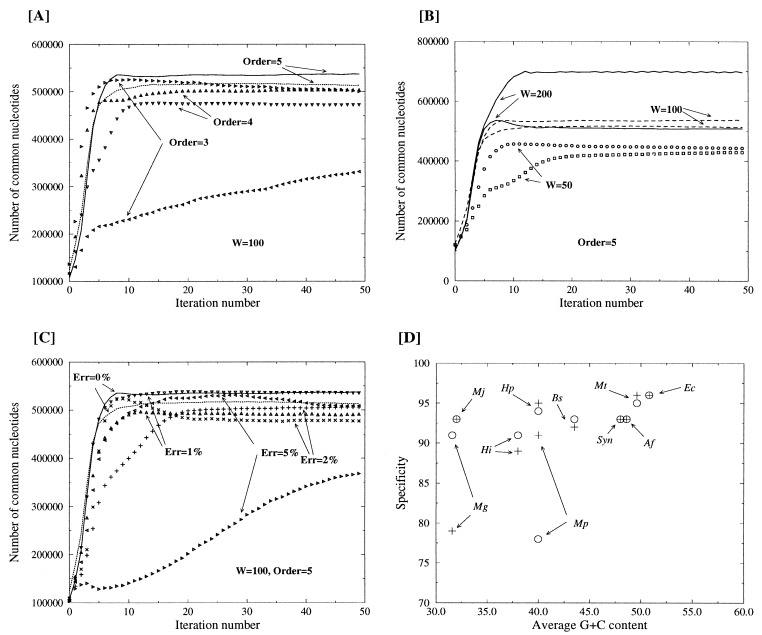
Figure 1.
Convergence of the iterative homogeneous Markov modeling. The numbers of nucleotides correctly assigned as “coding” or “reverse coding” are plotted to follow the convergence of the iterative procedure. (A) Influence of the Markov chain order. (B) Influence of the window size. (C) Influence of the simulated error rate. (D) Specificity of the recognition of coding (+) and reverse coding (o) segments for 10 genomes of different G+C content. Mj, M. jannaschii; Mg, M. genitalium; Mp, M. pneumoniae; Hi, H. influenzae; Hp, H. pylori; Bs, B. subtilis; Mt, M. thermoautotrophicum; Syn, Synechocystis sp.; Af, A. fulgidus; Ec, E. coli. The discrepancies between the recognition of coding and reverse-coding regions in the Mg and Mp genomes indicate an actual strand asymmetry.