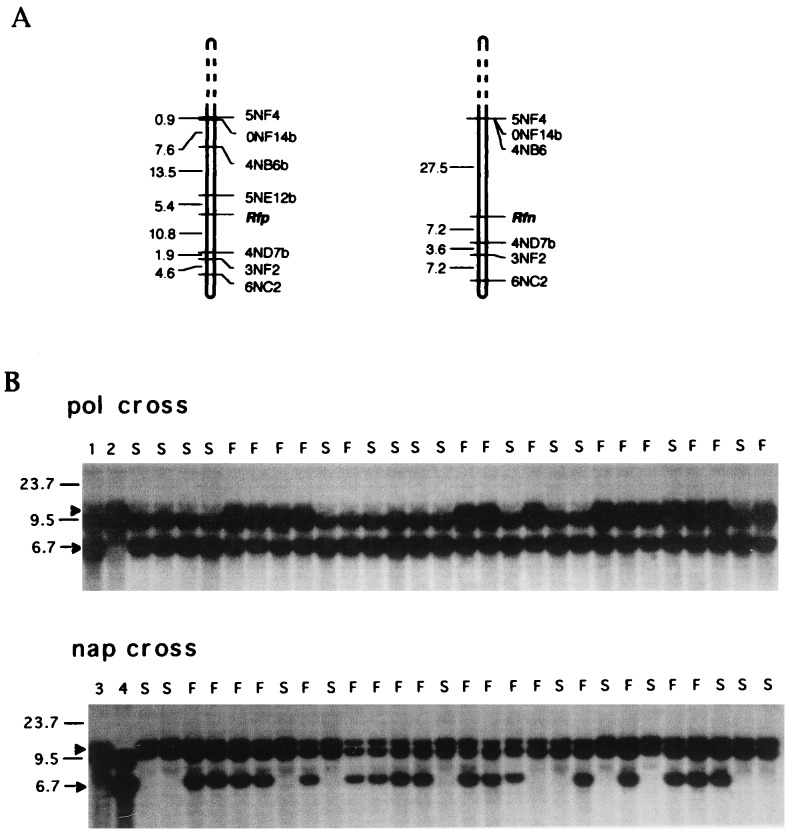
Figure 2.
RFLP mapping of Rfp and Rfn. (A) Maps of linkage group 18 in the vicinity of Rfp and Rfn constructed from backcross populations (described in B, below), which allowed segregation of Rfp (the pol cross, Left) and Rfn (the nap cross, Right) to be followed; note the similar map locations of the two restorer genes. The marker 5NE12b was not polymorphic in the nap cross and could not be mapped in this population. (B) A single RFLP marker detects alleles associated with both Rfp and Rfn. The RFLP marker 3NF2 (18) was used to probe EcoRV digests of genomic DNA from sterile (S) and fertile (F) individuals of two B. napus backcross populations. The pol cross allowed segregation of the pol restorer Rfp to be followed. It was generated first by crossing a Karat (pol) CMS plant (lane 1) with Westar-Rf (lane 2) and then crossing an F1 individual with the Karat (pol) parent; this corresponds to the KW population of Jean et al. (18). The nap cross (cross VI of Table 2) allowed segregation of the nap restorer Rfn to be followed. The genotype Karat (lane 4), which served as the CMS parent in the pol cross, was used as the source of the Rfn gene in a cross to male sterile Bronowski (nap) (lane 3). Note that the 10.0-kb fragment specific to Westar-Rf segregates with male fertility restoration (F) in the pol cross, where Karat was used as the CMS parent, whereas the 6.7-kb fragment specific to Karat segregates with male fertility restoration in the nap cross, where Karat was used as the fertility restored parent. Because 3NF2 maps approximately 10 cM from Rfp and Rfn, segregation with male sterility in both cases is incomplete.