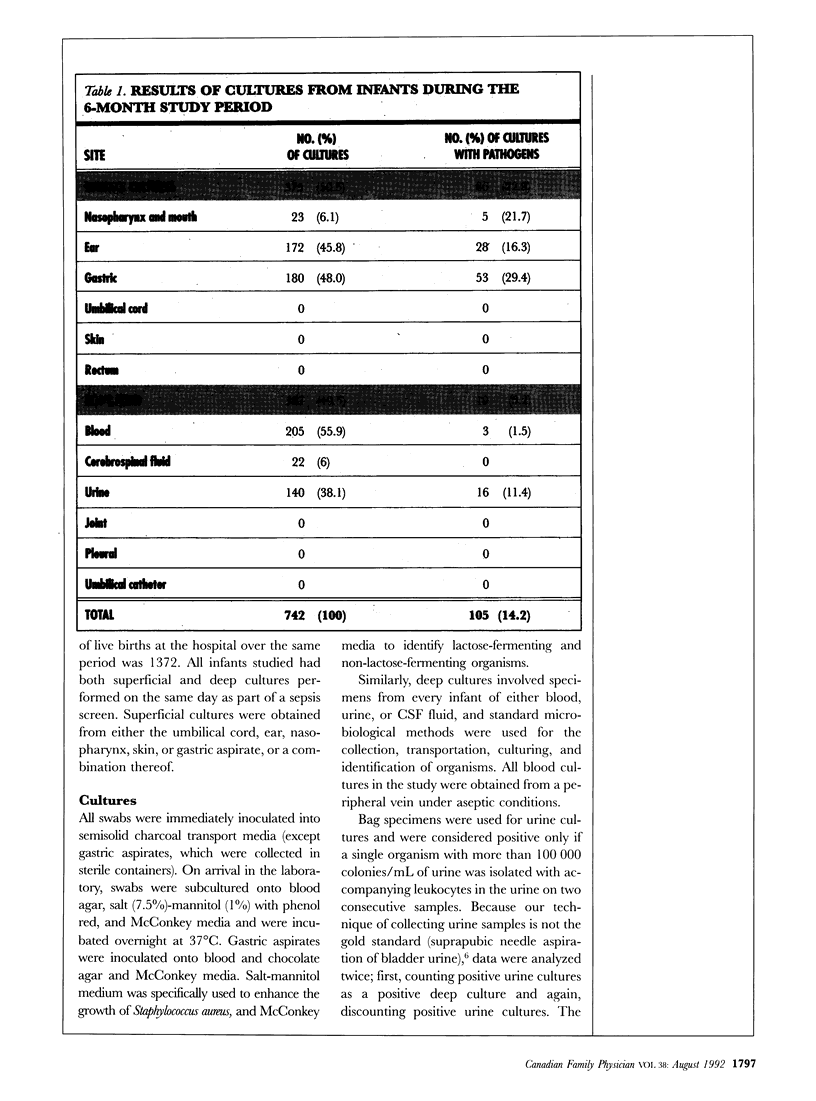
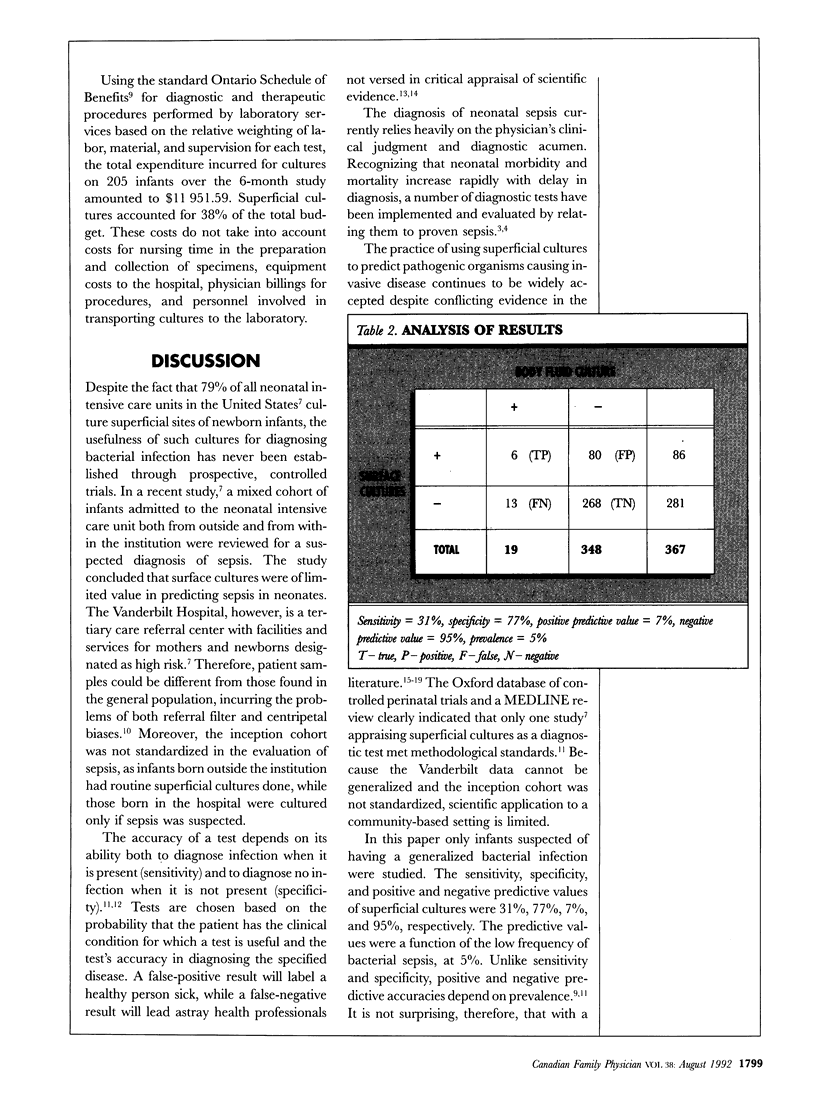
Abstract
In a study of babies younger than 2 weeks who were admitted to a community neonatal facility with suspected sepsis, pathogenic organisms grown from superficial swab samples were compared with those from deep cultures to meet the gold standard definition of true sepsis. We conclude that superficial cultures have limited value in the diagnosis of neonatal sepsis in a community setting.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brook R. H. Practice guidelines and practicing medicine. Are they compatible? JAMA. 1989 Dec 1;262(21):3027–3030. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns M. W., Burns J. L., Krieger J. N. Pediatric urinary tract infection. Diagnosis, classification, and significance. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1987 Oct;34(5):1111–1120. doi: 10.1016/s0031-3955(16)36321-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond M. F., Stoddart G. L. Economic analysis and clinical trials. Control Clin Trials. 1984 Jun;5(2):115–128. doi: 10.1016/0197-2456(84)90118-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. E., Schaffner W., Federspiel C. F., Cotton R. B., McKee K. T., Jr, Stratton C. W. Sensitivity, specificity, and predictive value of body surface cultures in a neonatal intensive care unit. JAMA. 1988 Jan 8;259(2):248–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griner P. F., Mayewski R. J., Mushlin A. I., Greenland P. Selection and interpretation of diagnostic tests and procedures. Principles and applications. Ann Intern Med. 1981 Apr;94(4 Pt 2):557–592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes R. B., Sackett D. L., Tugwell P. Problems in the handling of clinical and research evidence by medical practitioners. Arch Intern Med. 1983 Oct;143(10):1971–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanouse D. E., Jacoby I. When does information change practitioners' behavior? Int J Technol Assess Health Care. 1988;4(1):27–33. doi: 10.1017/s0266462300003214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomas J., Anderson G. M., Domnick-Pierre K., Vayda E., Enkin M. W., Hannah W. J. Do practice guidelines guide practice? The effect of a consensus statement on the practice of physicians. N Engl J Med. 1989 Nov 9;321(19):1306–1311. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198911093211906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mims L. C., Medawar M. S., Perkins J. R., Grubb W. R. Predicting neonatal infections by evaluation of the gastric aspirate: a study in two hundred and seven patients. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1972 Sep 15;114(2):232–238. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(72)90064-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NYHAN W. L., FOUSEK M. D. Septicemia of the newborn. Pediatrics. 1958 Aug;22(2):268–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philip A. G., Hewitt J. R. Early diagnosis of neonatal sepsis. Pediatrics. 1980 May;65(5):1036–1041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodwell R. L., Leslie A. L., Tudehope D. I. Early diagnosis of neonatal sepsis using a hematologic scoring system. J Pediatr. 1988 May;112(5):761–767. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(88)80699-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sackett D. L. Bias in analytic research. J Chronic Dis. 1979;32(1-2):51–63. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(79)90012-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprunt K. Practical use of surveillance for prevention of nosocomial infection. Semin Perinatol. 1985 Jan;9(1):47–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuerlein T. J., Butler J. C., Yeager T. D. Superficial cultures in neonatal sepsis evaluations. Impact on antibiotic decision making. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 1990 Aug;29(8):445–447. doi: 10.1177/000992289002900805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


