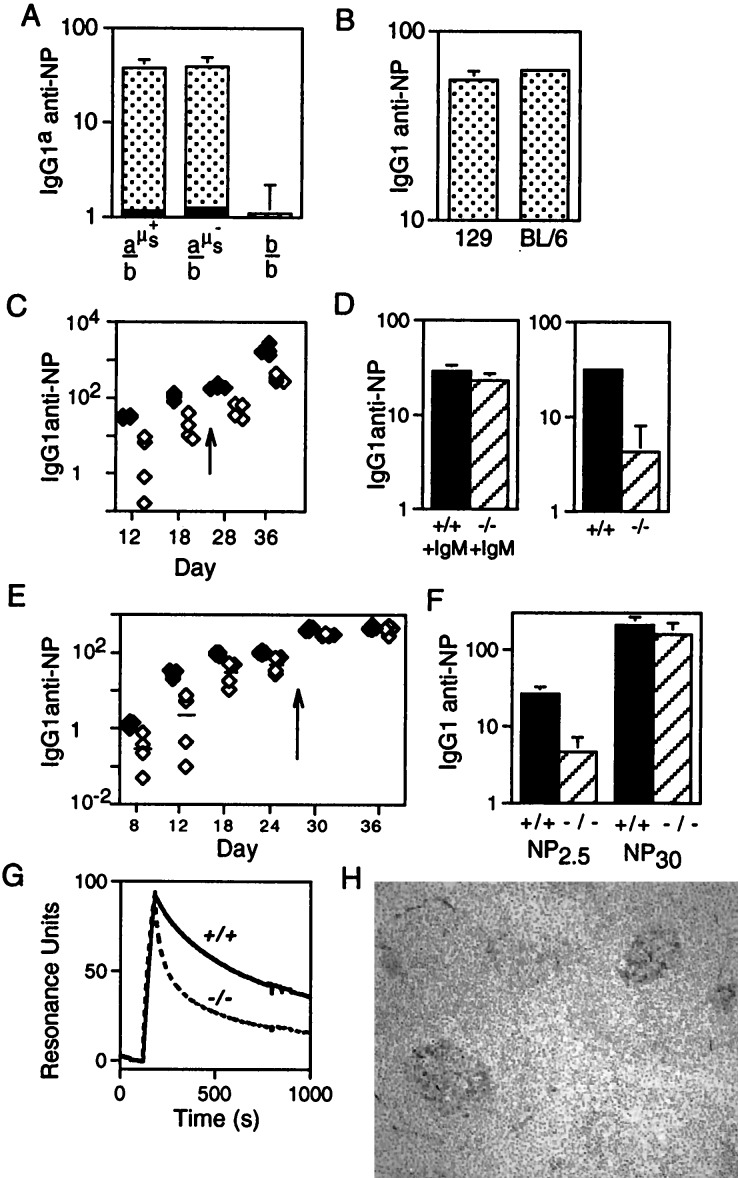
Figure 4.
T cell-dependent anti-NP responses. (A) Comparison of the day 12 IgG1a anti-NP response to NP-CG immunization in mice in which one IgH allele was of b allotype (derived from C57BL/6) and the other was either wild type a allotype (derived from 129; a-μs+), a allotype but carrying the targeted μs deletion (a-μs−), or b allotype (b). These mice (sets of four) were derived from breeding the ES cell-derived chimeras against C57BL/6. The solid section at the base of each histogram depicts the prebleed titer. The titers are given in arbitrary units as detailed under Materials and Methods. (B) Comparison of the day 12 total IgG1 anti-NP response to NP-CG immunization in 129 and C57BL/6 mice. (C) Comparison of the titers of IgG1 anti-NP antibody in μs−/− (open symbols) and wild-type mice (solid symbols) immunized with soluble NP-KLH and boosted (arrow) on day 24 as measured by ELISA on NP30-BSA-coated plates. Tail bleeds were obtained on the days indicated on the x axis. (D) Titers of IgG1 anti-NP antibody 12 days after NP-KLH immunization were compared in μs−/− and control mice in which the antigen challenge had been given together with pooled serum IgM from unprimed mice (an amount equivalent to the IgM present in 0.5 ml of serum). (E) Comparison of the titers of IgG1 anti-NP antibody in μs−/− (open symbols) and control littermates (solid symbols) immunized with alum-precipitated NP-CG and boosted (day 26) as monitored by ELISA on NP2.5-BSA-coated plates. (The magnitude of the day 12 IgG1 anti-NP response in NP13-CG immunized control mice is about 8-fold greater than in NP13-KLH mice when both are compared on NP30-BSA coated plates.) (F) Comparison of the titers of IgG1 anti-NP antibody in the day 12 serum of the NP13-CG immunized mice as assayed plates coated with NP2.5-BSA and NP30-BSA. (G) Analysis by surface plasmon resonance of the binding of serum antibody to NP6-BSA immobilized on the chip. The serum samples were obtained from μs−/− and μs+/+ siblings 12 days after challenge with NP-CG, and the 7S Ig fraction was purified as described in Materials and Methods. The bulk of the antibody in the μs− sample that is bound initially to the chip clearly has a dissociation rate severalfold higher than that in the control, although the heterogeneity of the serum antibody and resultant complexity of the dissociation curves preclude a simple calculation of koff. (H) Germinal centers in the spleens of μs−/− mice 12 days post-NP-CG immunization were visualized by staining for peanut agglutinin.