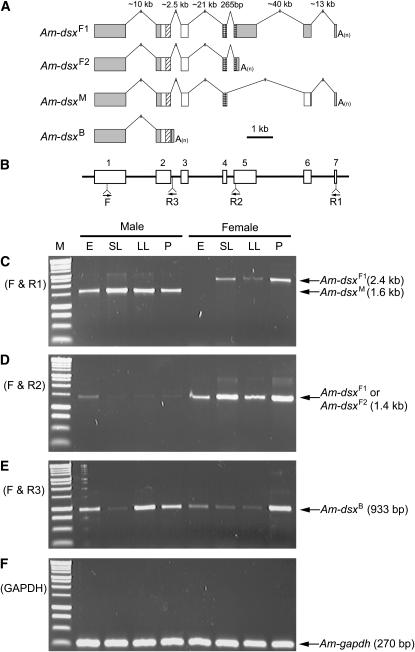
Figure 1.—
Gene structure and expression pattern of the four splicing variants of honeybee dsx. (A) Structures of the four splicing variants. Boxes represent exons and lines are introns. Only exons are drawn to scale. Shaded boxes are untranslated regions and open boxes are coding regions. Within coding regions, diagonally hatched boxes mark oligomerization domain 1/DNA-binding domain and cross-checked boxes mark oligomerization domain 2. “A(n)” represents the polyadenylated tail. (B) The locations of the primers used for RT–PCR experiments are shown as arrows. Open boxes are exons and lines are introns. They are drawn in alignment with the gene structures in A. The only forward primer (F) was designed to anneal to the first exon, which is shared by all four variants. R1 anneals to dsxF1 and dsxM, R2 to dsxF1 and dsxF2, and R3 to only dsxB. (C–F) RT–PCR amplicons from total RNA samples of four different developmental stages of both sexes are analyzed by 1% agarose gel electrophoresis. E, embryos; SL, small larvae; LL, large larvae; P, pupae. See materials and methods for detailed information on the samples. The leftmost lane (M) is the size standard (BenchTop 1-kb DNA ladder, Promega, Madison, WI). Names and sizes of amplicons are labeled with arrows. Primers F and R1 were used for C, F and R2 for D, and F and R3 for E. Primers for the honeybee glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase 1 gene were used as positive controls for F.