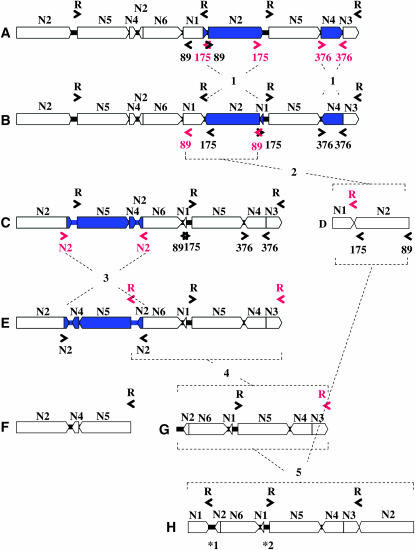
Figure 6.—
A proposed model for the evolution of the BGRC56777 mitochondrial master chromosome toward the TK81-O-like mitochondrial master chromosome. Three sets of inverted repeated sequences (89, 175, and 376 bp) were identified at the rearrangement breakpoints within the BGRC56777 mitochondrial genome (see also Figure 5), which are depicted in the linealized master chromosome A (581.9 kb). At the initial step (shown by 1), 175- and 376-bp repeated sequences (highlighted in red) recombined to introduce two inversions of the blue-colored regions, resulting in the isomeric master chromosome B. At the next step (shown by 2), 89-bp repeated sequences (highlighted in red) recombined to loop out 135.2-kb subgenomic molecule D. The remaining 446.7-kb molecule C was further converted to the isomeric molecule E by the recombination via truncated N2 repeated sequences (highlighted in red) at step 3. The molecule E was then split into two molecules, F (195.5 kb) and G (251.2 kb), by the recombination-active repeats R containing rrn26 (highlighted in red) at step 4. The molecules D and G were fused by the recombination mediated by R (highlighted in red) to yield TK81-O-like master chromosome H (386.4 kb) at step 5. *1 and *2 (parts of region 2) indicate the position of sequences unique to the 386.4-kb molecule.