Fig. 2.
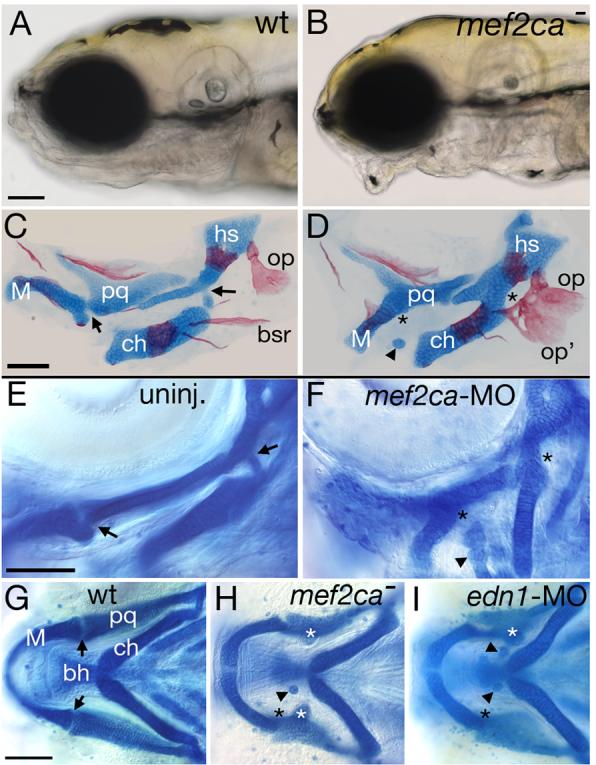
Reduction of mef2ca function causes facial deformities which phenocopy partial edn1 loss-of-function. (A-B) Live phenotypes of mef2ca mutants at 5 dpf. mef2ca mutants have malformed faces, open mouths, and ventrally displaced jaws. (C-D) Cartilage and bone phenotypes in the pharyngeal arches of mef2ca mutants. Dorsal/ventral joints (arrows) are missing in mef2ca mutants (asterisks). Mutants also have ectopic cartilage nodules (arrowhead), distinctive ectopic medial processes emanating from the upper jaw cartilage (see Table 2) and homeotic transformations of hyoid dermal bone identity. In mef2ca mutants, a ventral hyoid bone, the branchiostegal ray, is enlarged, assumes the shape of and fuses to the dorsal hyoid bone, the opercle. (E-F) mef2ca-MO injection phenocopies mef2ca mutations. Lateral views of wholemount 4.5 dpf wild-type larvae, uninjected (E) and injected with 5 ng of mef2ca morpholino (F). mef2ca-MO injected fish display characteristic mef2ca mutant cartilage phenotypes. Joints are lost (asterisks) and ectopic cartilage nodules (arrowhead) are seen near the basihyal. (G-I) mef2ca mutation phenocopies gradual reduction in edn1 function. Ventral views of 4.5 dpf Alcian stained wild-type (G), mef2cab631 mutant (H), and low level edn1-MO injected (I) larvae. mef2ca mutants and low level edn1-MO morphants display joint loss (black asterisks), ectopic medially-projecting processes on the upper jaw cartilage, the palatoquadrate (white asterisks), and ectopic cartilage nodules near the basihyal (arrowheads). bh, basihyal; bsr, branchiostegal ray; ch, ceratohyal; hs, hyosymplectic; M, Meckel's; op, opercle; pq, palatoquadrate.
