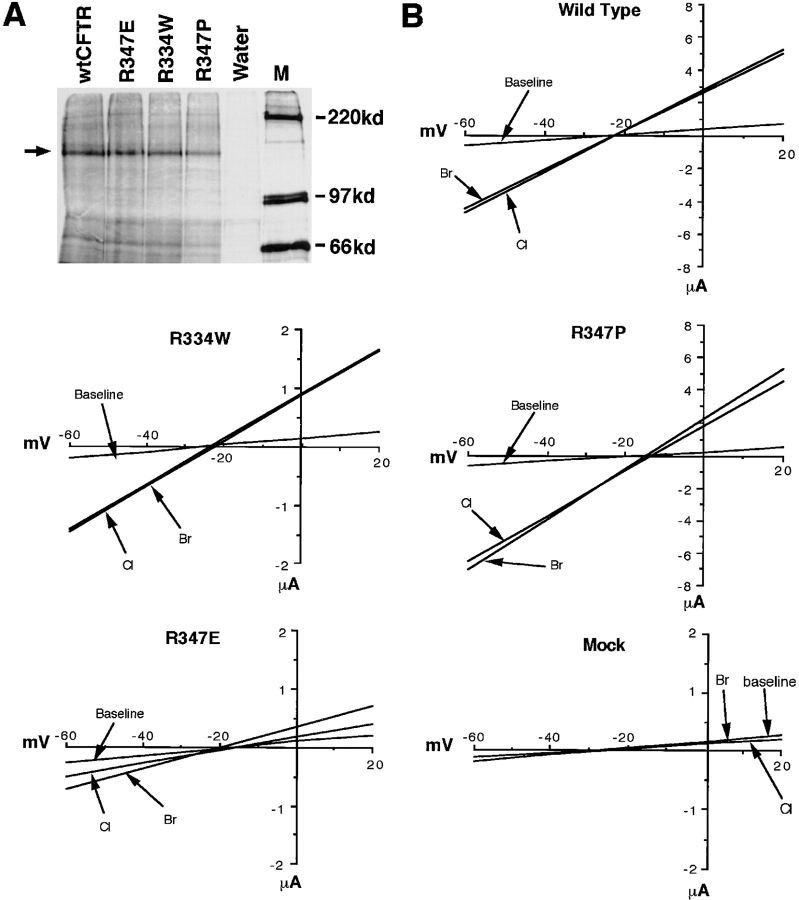
Figure 6.
Electrophysiological properties of CFTR mutants using Wc two-electrode voltage clamp measurements. Mutants of CFTR that alter charged arginine residues within the channel pore including R334W, R347E, and R347P were used. A demonstrates the amount of [35S]methionine-labeled CFTR immunoprecipitated with anti-hCFTR antibodies from oocytes injected with mutant and wild-type CFTR cRNAs. The arrow depicts unglycosylated CFTR protein produced 3 h after injection. The Wc I/V relationships for wtCFTR, R347P, R347E, R334W cRNA, and water-injected oocytes are given in B. Arrows denote the I/V relations before forskolin/IBMX activation in the presence of extracellular Cl− (marked baseline) and after adding forskolin/ IBMX in the presence of extracellular Cl− (Cl) and bromide (Br). Stimulation of CFTR was performed by perfusion of the oocyte with appropriate buffers containing 100 μM IBMX and 10 μM forskolin. ND96 buffer was used throughout the experiment where NaBr replaced NaCl for halide selectivity measurements. The order of buffer perfusion was as follows: (a) ND96 (NaCl); (b) ND96 (NaCl) + forskolin/IBMX; and (c) ND96 (NaBr) + forskolin/IBMX. These results depict average I/V relationships from N experiments for wtCFTR (N = 5), R347E (N = 5), R347P (N = 5), R334W (N = 8), and water (N = 7)-injected oocytes from at least two independent batches of oocytes.