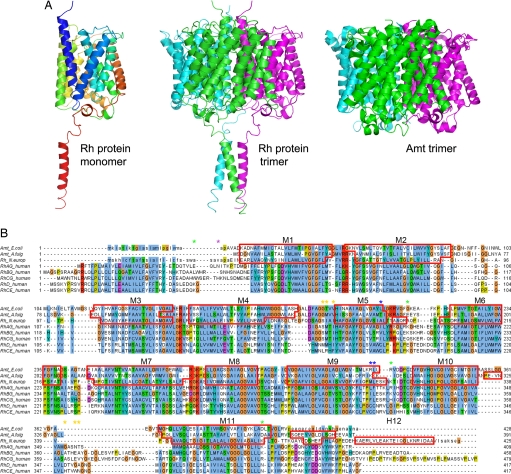
Fig. 1.
Structure of the N. europaea Rh protein. (A Left) Ribbon diagram of N. europaea Rh protein subunit colored in rainbow from blue to red. (A Center) Ribbon diagram of N. europaea Rh protein trimer colored by subunit. (A Right) Ribbon diagram of E. coli AmtB colored by subunit. Note the additional C-terminal helix on the Rh protein. The diagram is oriented such that the periplasmic surface is on the top and the cytoplasmic face is on the bottom. (B) Sequence alignment of the N. europaea Rh protein to the E. coli AmtB and A. fulgidus Amt1 based on their respective structures and to the five human Rh proteins based on the program ClustalW (34). The residues not observed in the Rh protein structure are shown in lowercase. Segments assigned to α-helices are framed with red lines. Asterisks mark topologically relevant residues: glycosylation and protease sensitive sites on RhAG are indicated with purple and green asterisks, respectively; highly antigenic and potentially palmitoylated residues of RhD are labeled with orange and blue asterisks.