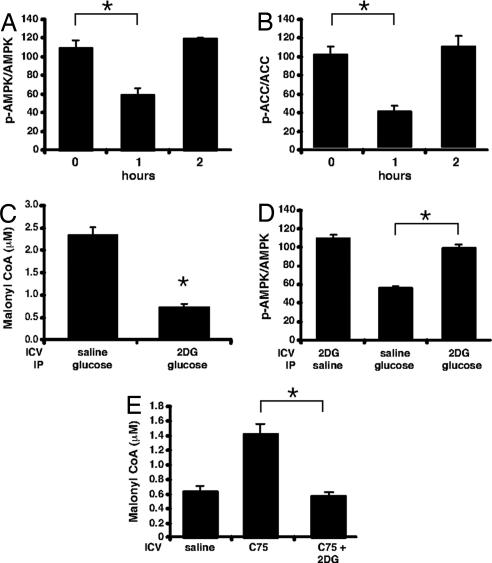
Fig. 3.
Dependence of hypothalamic AMPK phosphorylation status on plasma glucose level. Mice deprived of food for 20 h were given an i.p. injection of glucose (4 g/kg of body weight). Hypothalami were collected in RIPA buffer, and SDS/PAGE was performed with total AMPK and phosphospecific AMPK (A) or total ACC and phosphospecific ACC antibodies (B) shown as the ratio of phosphoprotein/total (n = 3 per group). (C) Mice deprived of food for 20 h were given 2 μl of vehicle or 5 mM 2-deoxyglucose i.c.v. and an i.p. dose of vehicle or glucose (4 g/kg of body weight). Hypothalami were collected at 1 h, and malonyl-CoA was determined (n = 4 per group). (D) Mice deprived of food for 20 h were given 2 μl of vehicle or 5 mM 2-deoxyglucose i.c.v. and an i.p. dose of vehicle or glucose (4 g/kg of body weight). Hypothalami were collected at 1 h, and SDS/PAGE was performed with total AMPK and phosphospecific AMPK antibodies shown as above (n = 3 per group). (E) Mice deprived of food for 20 h were given vehicle or 2 μl of C75 (5 mg/ml) or C75 and 5 mM 2-deoxyglucose i.c.v. Hypothalami were collected at 2 h. *, P < 0.002.