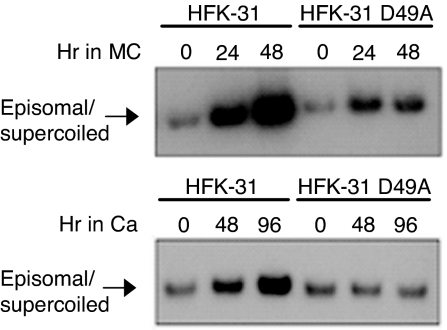
Fig. 6.
Mutation of the E1 caspase cleavage site reduces differentiation-dependent viral genome amplification. HFKs that stably transfected with WT 31 genomes or genomes containing the E1 D49A caspase cleavage mutant were suspended in methylcellulose for 24 and 48 h (Upper) or grown in high calcium for 48 and 96 h (Lower) to induce differentiation. DNA was harvested from undifferentiated, monolayer cultures (T0) and differentiated cells at the indicated times. Southern blot hybridization was performed by using the HPV genome as a probe. A minimum of three independent experiments were performed by using three different HFK backgrounds.