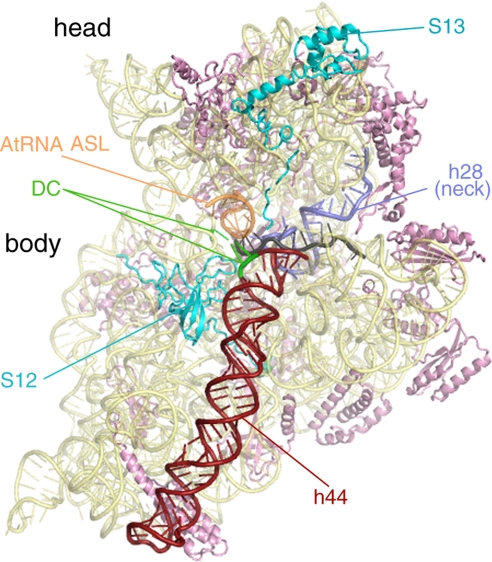
Fig. 1.
Atomic model of the 30S subunit of the pretranslocational ribosome from Thermus thermophilus (ref. 34; Protein Data Bank ID code 2J00). This intersubunit view of the 30S highlights several important features, which are color-coded and labeled. Ribosomal proteins S12 and S13 interact directly with the 50S subunit and affect ratcheting efficiency of the ribosome. The mRNA channel passes between the head and the body of the SSU (mRNA is colored gray). Upon EF-G binding, the top of helix 44 (h44) bends from the A site toward the P site. Because helix 44 is directly connected to helix 28 (h28 or the “neck”), the movement in h44 could provide torsional force on h28. GTP hydrolysis by EF-G decouples the tether between the A-site tRNA bound to the head and the decoding center (DC) in the body of the SSU. This event would release the head to rotate about its neck and relieve the torsional force in h28. The head rotation is likely to be important for movement of the mRNA and tRNA anticodon stem-loops on the SSU.