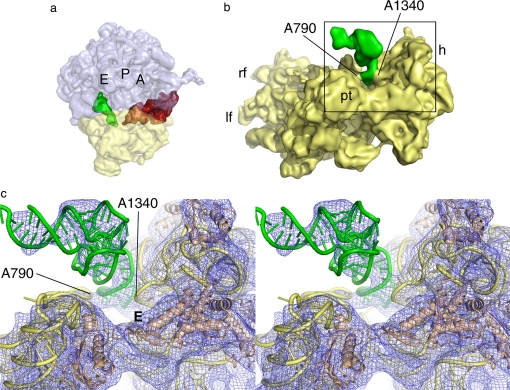
Fig. 4.
The P/E-site tRNA visualized in cryo-EM reconstructions. (a) A side view of the 80S·ADPR-eEF2·GDPNP complex (23), showing the CCA end of the tRNA occupying the E site of the large subunit, while the anticodon stem-loop occupies the P site of the small subunit. The A, P, and E sites of the ribosome are individually labeled. (b) The anticodon stem-loop of the P/E-site tRNA forms a strong interaction with the small subunit head, near the G1338-U1341 ridge, and a weaker interaction with the small subunit body, via the A790 loop of the 18S rRNA. The gap between A790 and A1340 separates the ribosomal P and E sites of the small subunit. (c) Stereo view of the interactions between the small subunit and P/E-site tRNA described in b. The head of the small subunit in this complex is rotated, increasing the distance between A790 in the body and A1339 in the head of the small subunit from ≈18 Å to ≈26 Å. This distance would allow passage of the anticodon stem-loop from the P to the E site; however, the tRNA remains bound in the hybrid state. Passage of the tRNA anticodon stem-loop from the P to the E site of the small subunit therefore must occur during back-ratcheting and back-rotation of the head of the small subunit, once EF-G/eEF2 dissociates from the ribosome. E denotes the E site of the small subunit.