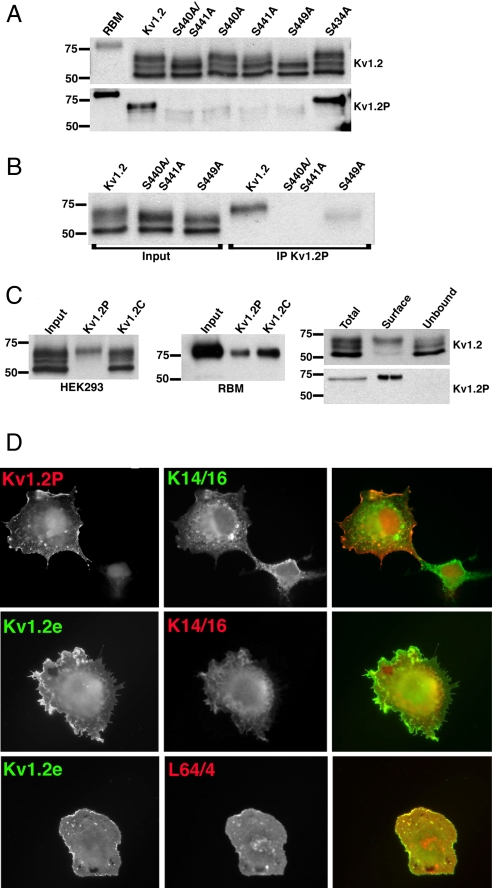
Fig. 3.
Phosphospecific Abs Kv1.2P and L64/4 specifically recognize cell-surface Kv1.2. (A) Immunoblot analysis performed against RBM prepared from postnatal day 15 (P15) brain and lysates from HEK293 cells expressing WT Kv1.2 and phosphorylation site mutants S440A/S441A, S440A, S441A, S449A, and S434A. Shown is immunoreactivity using the general anti-Kv1.2 mAb K14/16 (Upper) and using the pS440/pS441-specific Kv1.2P rabbit Ab (Lower). (B) Input into and products of immunoprecipitation reactions performed with Kv1.2P Ab on lysates from HEK293 cells expressing WT Kv1.2, S440A/S441A, and S449A and blotted with K14/16. (C) (Left) Input into and products of immunoprecipitation reactions performed with Kv1.2P and Kv1.2C Abs on lysates from HEK293 cells expressing WT Kv1.2, and blotted with K14/16. (Center) Input into and products of immunoprecipitation reactions performed with Kv1.2P and Kv1.2C Abs on lysates of RBM as assessed by immunoblotting with K14/16 Ab. (Right) Cell surface biotinylated (Surface) and intracellular nonbiotinylated (Unbound) pools of WT Kv1.2 in HEK293 cells were isolated by surface biotinylation and streptavidin–agarose enrichment/depletion, respectively, from a total biotinylated cell lysate (Total). Fractions were immunoblotted for total Kv1.2 with K14/16 (Upper) and with Kv1.2P (Lower) Abs. Numbers on the left in all immunoblots refer to the molecular weight of prestained molecular weight standards. (D) COS-1 cells transfected with WT Kv1.2 were double immunofluorescence stained with K1.2P (red) and K14/16 (green) after permeabilization (Top), with Kv1.2e (green) before and K14/16 (red) after permeabilization (Middle), or Kv1.2e (green) before and L64/4 (red) after permeabilization (Bottom).