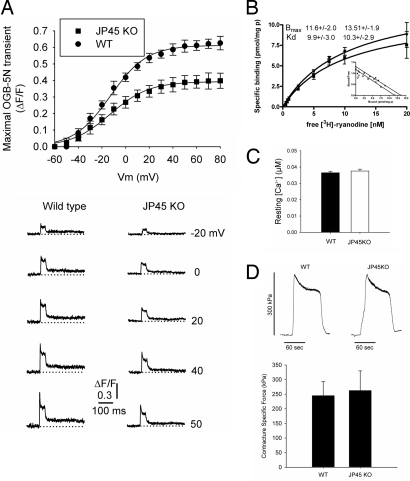
Fig. 5.
Ablation of JP45 reduced maximal voltage-dependent SR Ca2+ release. (A Upper) SR Ca2+ release in FDB fibers from wild-type (n = 17) and JP45 KO (n = 20) mice. Data points (mean ± SEM) were fitted to a Boltzmann equation. (A Lower) OGB-5N transients in FDB fibers from wild-type and JP45 KO mice in response to various command pulses corresponding to the steepest part of the fluorescence/membrane voltage relationship. (B) [3H]Ryanodine binding to heavy SR fractions from wild-type and JP45 KO mice. Points represent the mean ± SD of five to eight determinations in two different R4 fraction preparations. (C) Fura-2 resting Ca2+ concentration measurements in FDB fibers from wild-type (n = 72 fibers) and JP45 KO (n = 71) mice did not differ significantly. (D Upper) Typical contractures in response to 1 mM 4-CmC in FDB fibers from wild-type (n = 8) and JP45 KO (n = 11) mice. (D Lower) Differences are not statistically significant.