Fig. 2.
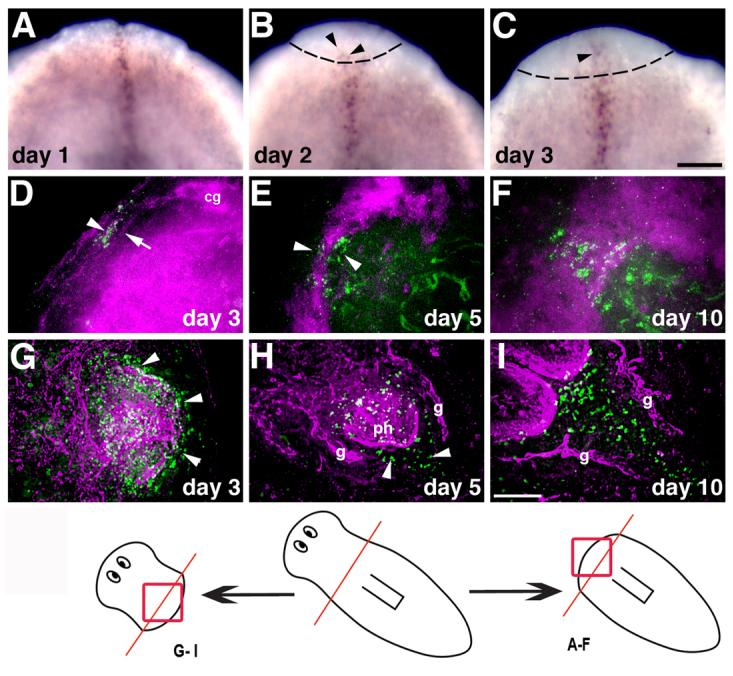
Expression of Smed-slit during regeneration. (A-C) Whole-mount in situ hybridization to detect Smed-slit mRNA during anterior regeneration; days after amputation (prepharyngeal) are indicated. Arrowheads in (B) and (C) point to Smed-slit-positive cells within the blastema, which is delimited by dotted lines. (D-I) Double labeling to detect Smed-slit mRNA (in green) by fluorescent in situ hybridization and anti-phospho-tyrosine immunofluorescence (in magenta) during anterior regeneration (D-F) and posterior regeneration (G-I). Arrowheads in (D) and (E) indicate Smed-slit-positive cells; arrow in (D) points to thin processes that connect the left and right halves of the new cephalic ganglia. Arrowheads in (G) indicate Smed-slit expression in the pharynx primordium. Arrowheads in (H) point to Smed-slit positive cells in the new post-pharyngeal region. The drawing at the bottom of the figure indicates the regions shown in the indicated panels; the prepharyngeal amputation site is shown in red. Abbreviations: cg, cephalic ganglia; g, gut; ph, pharynx. (A-C) anterior to the top; (D-I) anterior to the top left corner. Scale bars: 100 μm in A-C ; 50 μm in D-I.
