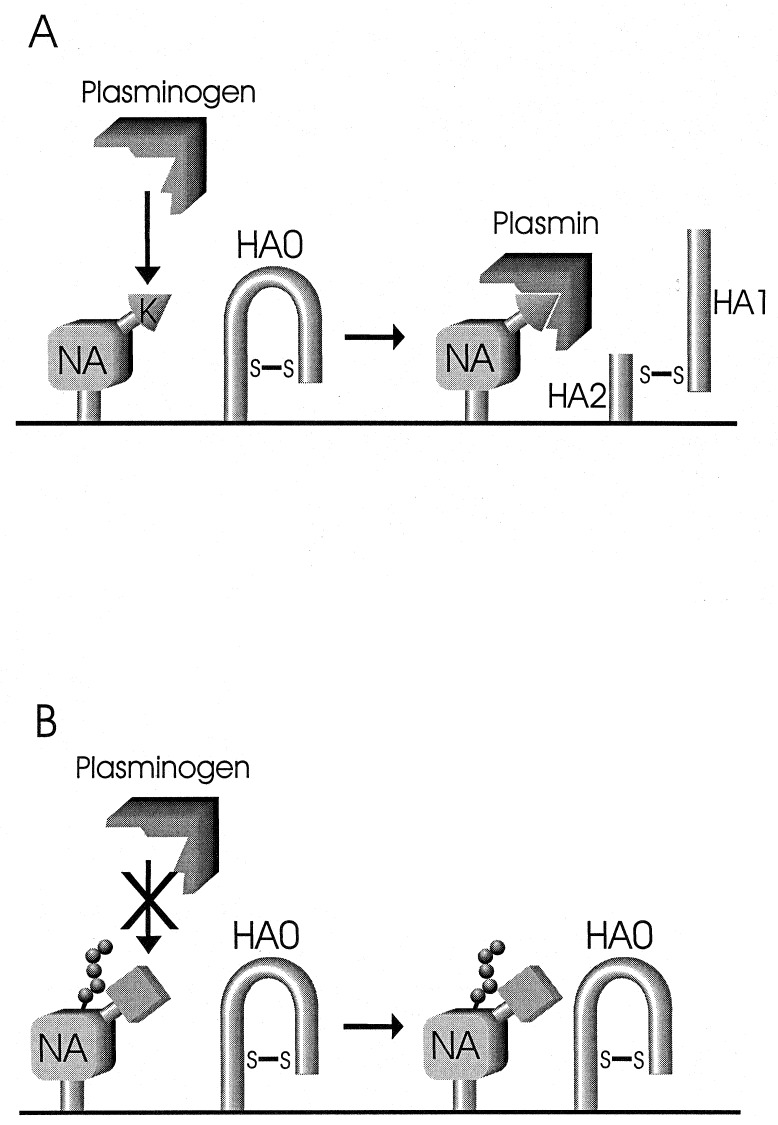
Figure 5.
Schematic representation of plasminogen-mediated HA cleavage. (A) Plasminogen binds to a lysine at the carboxyl terminus of the WSN NA. Bound plasminogen is activated to plasmin by a plasminogen activator (most likely of cellular origin). Enzymatically active plasmin then cleaves HA0 into HA1 and HA2 subunits. (B) If NA does not contain a lysine at the carboxyl terminus or an oligosaccharide chain is present in the vicinity, plasminogen does not bind to the NA and HA0 remains uncleaved.