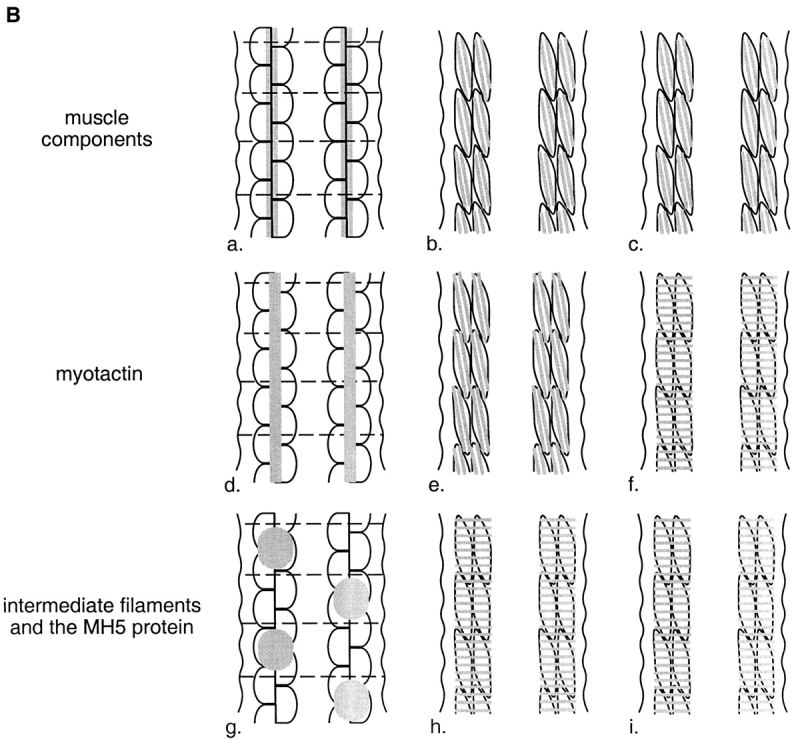
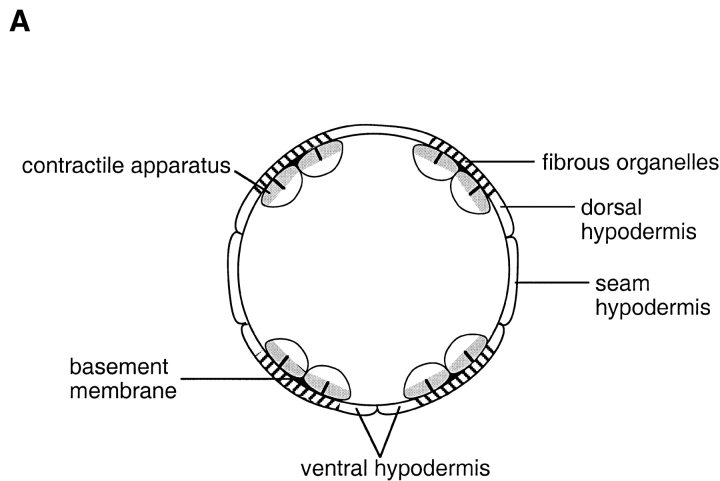
Figure 1.
(A) Schematic representation of a cross-section through a threefold stage embryo depicting the spatial relationships between the contractile apparatus of the bodywall muscle (oval-like shapes), the muscle basement membrane (black) and hypodermal fibrous organelles (hatched areas). Dorsal is toward the top of the page. The four muscle quadrants are shown, each consisting of two rows of muscle cells, with the long axis of the cells perpendicular to the page. The contractile apparatus is restricted to the portion of the muscle cell closest to the muscle cell membrane facing the hypodermis. Hypodermal fibrous organelles are restricted to the region of the hypodermis adjacent to bodywall muscle cells. A specialized basement membrane, positioned between muscle cells and the hypodermis, helps to anchor muscle cells. Myotactin is thought to be an integral membrane protein expressed on the basal hypodermal membrane with its large extracellular domain extending into the basement membrane toward the adjacent muscle cells. (B) Schematic representations of the localization of muscle, fibrous organelle–associated intermediate filaments, the MH5 protein and myotactin in dorsal views of progressively older embryos. Intermediate filament proteins and the MH5 protein, an immunologically defined protein that localizes near fibrous organelles, show the same distribution at all developmental stages. Schematics a, d, and g represent an early stage of development (just before the start of elongation); b, e, and h represent an intermediate stage (twofold); and c, f, and i represent a later stage (threefold). In each schematic (a–i) a portion of the two dorsal muscle quadrants is shown. Each quadrant consists of two rows of mononucleated muscle cells with the long axis of the cells oriented along the anterior-posterior axis of the worm. Anterior is toward the top of the page. Wavy, black, vertical lines mark the lateral edges of the dorsal hypodermis. Horizontal, dashed black lines in a, d, and g represent the boundaries between adjacent dorsal hypodermal cells. These lines do not appear in b, c, e, f, h, and i because at these later developmental stages the dorsal hypodermal cells have fused to form a syncytium. Gray areas represent the localization of components of the muscle cell contractile apparatus (a–c), myotactin (d–f), and the fibrous organelle–associated intermediate filaments and MH5 protein (g–i). Schematics a–c are focused on the plane of the muscle cells, while d–i are focused on the dorsal hypodermal cells. Although we discuss only the dorsal surface of the embryo, similar events occur on the ventral surface. At stages earlier than those shown, muscle cells are adjacent to lateral (seam) hypodermis, and muscle proteins are diffusely distributed in muscle cells. Similarly, the hypodermal proteins are diffusely distributed in dorsal hypodermal cells. As muscle cells migrate to contact dorsal hypodermal cells, muscle components accumulate at the membrane where muscle cells contact each other and the hypodermis (a). At about the same time, myotactin, intermediate filament proteins and the MH5 protein are recruited to specific regions of the hypodermis adjacent to some muscle cells. Myotactin accumulates adjacent to where the contractile apparatus is forming (d) while intermediate filaments and the MH5 protein accumulate in a single broad patch in each hypodermal cell adjacent to one muscle quadrant (g). By the twofold stage, the sarcomeric organization of the obliquely striated muscle is observed (b). At this stage myotactin is still adjacent to the forming contractile apparatus and in fact is organized into rows of dots running oblique to the long axis of the worm and following the oblique striations of the muscle (e). In contrast, intermediate filaments and the MH5 protein are organized in circumferentially oriented bands that are restricted to the small regions of the hypodermis adjacent to muscle (h). During the threefold stage, myotactin colocalizes with intermediate filaments and the MH5 protein (f and i).