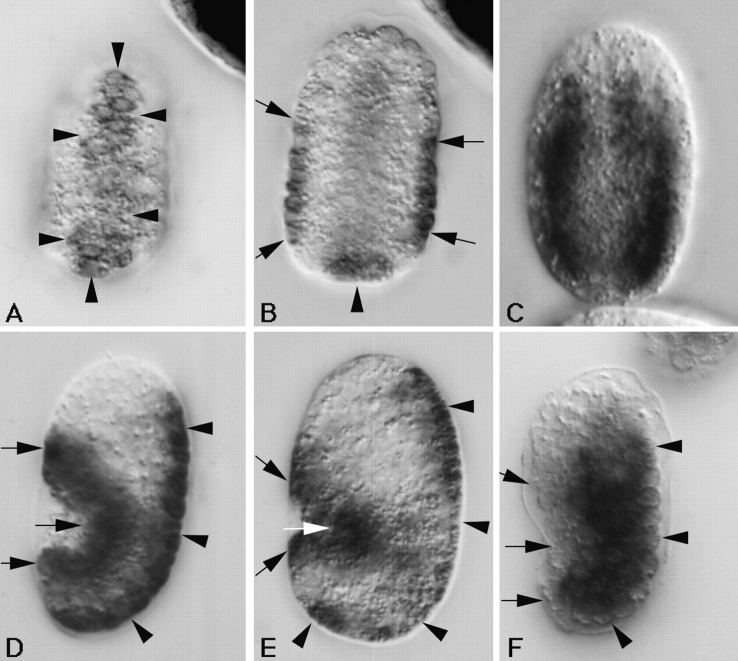
Figure 6.
Embryonic expression of the myotactin gene assayed by in situ hybridization. Mixed stage embryos were fixed and incubated with anti-sense myotactin (A, B, D, and E) or myosin (C and F) single stranded DNA probes labeled with digoxigenin. Probes were visualized using an alkaline-phosphatase-conjugated anti-digoxigenin antibody. Anterior is toward the top and in D–F dorsal is to the right. Arrowheads designate dorsal hypodermal cells and arrows designate ventral hypodermal cells. (A) Dorsal and (B) mid-focal plane images of the same <290-min embryo. The anti-sense myotactin probe is detected on the dorsal surface of the embryo (A) and in cells at the lateral edges (B) of the embryo. These cells are the dorsal and ventral hypodermal cells, respectively. (C) Mid-focal plane of a 300-min embryo. The myosin probe is detected in the bodywall muscle cells giving a different pattern from that of the myotactin probe (compare to B). (D) Lateral view of a 320-min embryo and (E) lateral view of a comma stage embryo (390 min). Anti-sense myotactin probe is detected at the dorsal (dorsal hypodermal cells) and ventral (ventral hypodermal cells) edges of the embryo. (F) Lateral view of a 320-min embryo. The myosin probe is detected in bodywall muscle cells. The positive cells are away from the dorsal and ventral edges of the embryo. Embryos hybridized with either myosin or myotactin sense probes showed no staining.