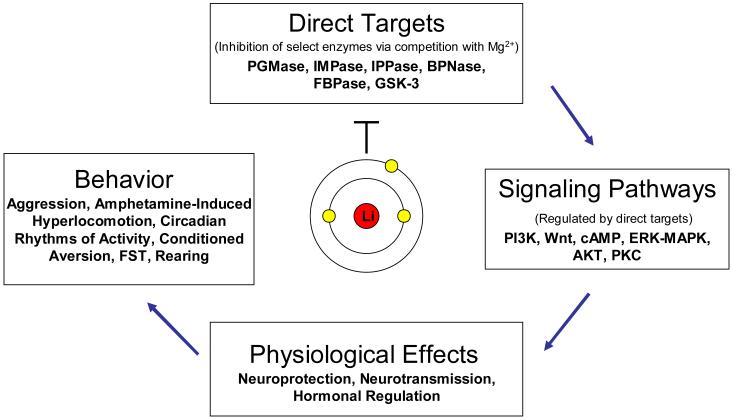
Figure 1. Lithium: loci of preclinical research.
The mechanism by which lithium exerts its therapeutic effects is investigated from a number of perspectives. The cation directly inhibits a select group of enzymes, included in which are inositol monophosphatase (IMPase), inositol polyphosphate 1-phosphatase (IPPase), phosphoglucomutase (PGMase), biphosphate nucleotidase (BPNase), fructose 1,6-biphosphatase (FBPase), and glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3). The study of these direct targets can provide insight to the ability of lithium to modulate intracellular signaling cascades, the downstream consequences of which are its effects on physiology and behavior. Ideally, the study of behavior will in turn provide insight on which of the immediate targets of lithium is relevant to its therapeutic effects. Abbreviations: cAMP: cyclic adenosine monophosphate; ERK-MAPK: extracellular signal-regulated kinase-mitogen-activated protein kinase; FST: forced swim test; PI3K: phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; PKC: protein kinase C.