Figure 1.
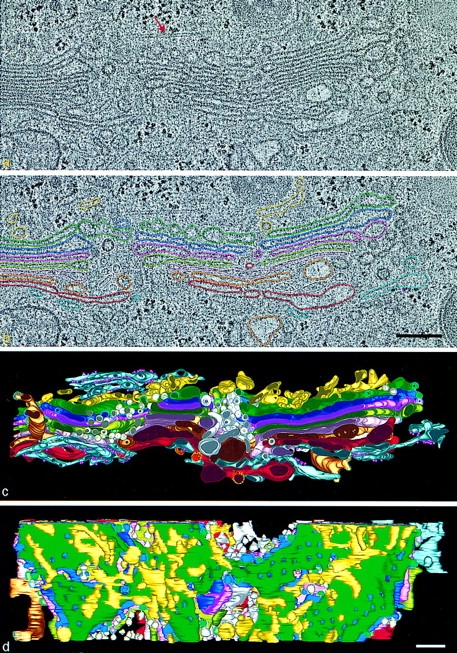
HVEM tomographic reconstruction of a portion of the Golgi ribbon from a fast frozen, freeze-substitution fixed NRK cell. Two serial 4-nm slices extracted from the tomogram are shown in a and b. Comparison of the images shows how little is changed from one such slice to its neighbor; e.g., the position of the microtubule (red arrow). (a) Membranes of individual Golgi and ER cisternae are clearly seen. (b) In analyzing the data, different cisternae were modeled by placing points along the membranes that delimit them, connecting the points with colored line segments, and building closed contours that model the different membrane compartments of a given slice. c and d are renditions of the surfaces fit to all of the contours for each object modeled in this Golgi region. The model viewed in c is in the same orientation as the tomographic slices. d shows a cis-side view with the cis ER removed to provide a better view of the ERGIC elements and the underlying Golgi cisternae. The 44 elements of the ERGIC are discontinuous, display no coated budding profiles, and do not appear to be flattened against the cis-most cisterna. Free vesicles in wells and the NCR (white) have unrestricted access to the cis side of the stack. The colors used to represent different components of the model are the same in all figures: ER, blue-gray; ribosomes, small purple spheres; ERGIC, yellow; Golgi cisterna: C1, green; C2, purple; C3, rose; C4, olive; C5, pink; C6, bronze; C7, red. Polymorphic structures in the NCR are light pink and gold. Non–clathrin-coated budding profiles on cisternae C1–C6, blue stippling. Clathrin-coated buds on C7, yellow stippling. Bars, 250 nm.
