Figure 8.
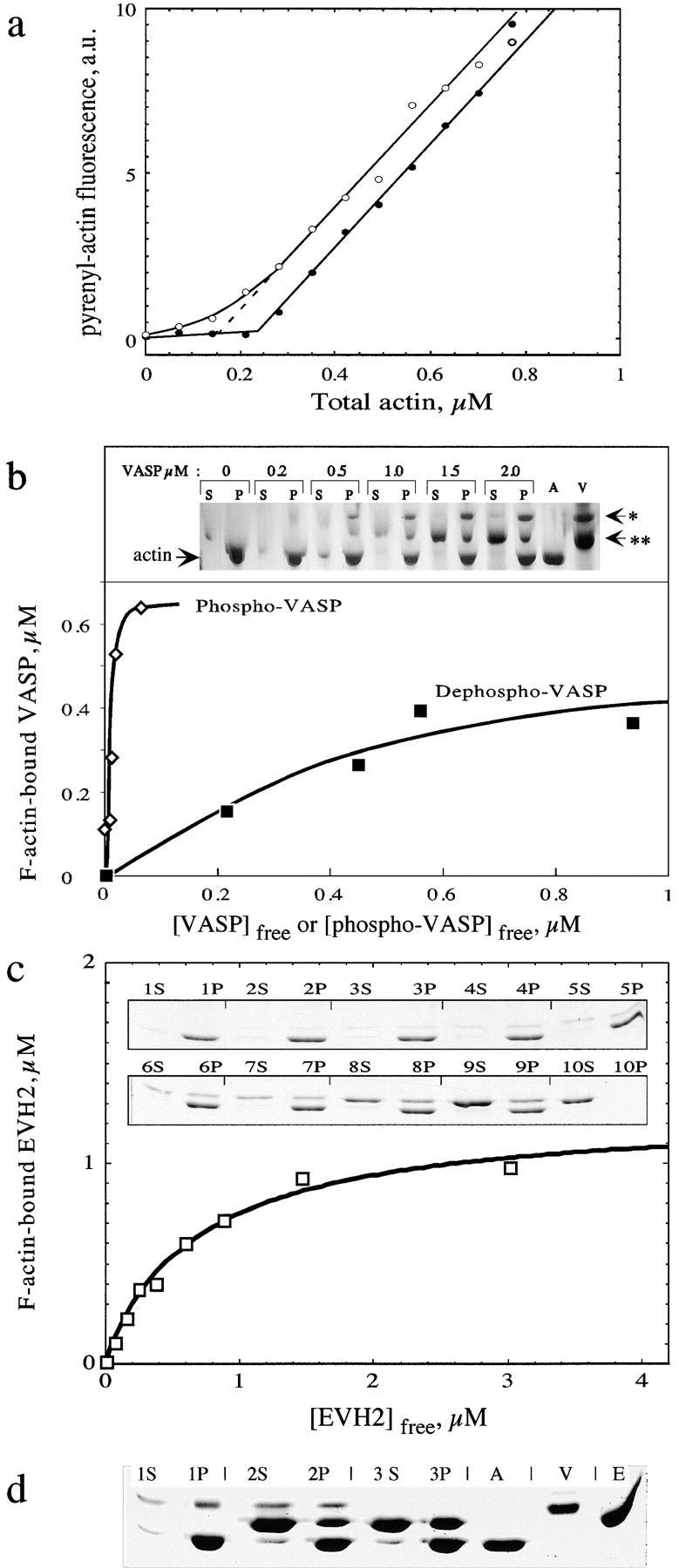
VASP binds to and stabilizes F-actin in a phosphorylation-regulated manner. (a) VASP shifts the critical concentration plots for actin assembly toward a lower value. Critical concentration plots for polymerization of Mg-actin in the absence (filled circles) and presence (open circles) of 1 μM eukaryotic recombinant VASP. Pyrenyl-labeled actin was polymerized at a high concentration and serially diluted in buffer adjusted to the following ionic conditions: 5 mM Tris-Cl−, pH 7.5, 0.2 mM ATP, 0.1 mM CaCl2, 0.2 mM EGTA, 0.1 mM MgCl2, 1 mM DTT, 2 mM Hepes, 15 mM NaCl, and 1% glycerol. (b) Sedimentation assay for the binding of eukaryotic recombinant VASP to F-actin. Mg-F-actin was polymerized under physiological ionic conditions (0.1 M KCl, 1 mM MgCl2) and mixed at 1 μM with VASP at the indicated concentrations. Samples were centrifuged for 30 min at 400,000 g, 20°C. Pellets were resuspended in G buffer at the original volume. Pellets (P) and supernatants (S) were submitted to SDS-PAGE. A, actin alone (1 μM); V, VASP alone (2 μM); *, 50-kD band corresponding to serine 157–phosphorylated VASP; **, 46-kD band corresponding to serine 157–unphosphorylated VASP. Data are plotted as bound VASP versus free VASP. The concentrations of free and F-actin–bound VASPs were derived from the scanning of the gels (see Materials and Methods). The curves represent the fit to the data using values of equilibrium dissociation constants K Y = 22 nM and K X = 0.8 μM for phospho- and dephospho-VASP, respectively (see text). (c) Sedimentation assay for EVH2 binding to F-actin. F-actin (1 μM) polymerized in physiological ionic conditions was incubated with EVH2 at the following concentrations in μM: 1, 0; 2, 0.25; 3, 0.5; 4, 0.75; 5, 1.0; 6, 1.5; 7, 2; 8, 3; 9, 5; 10, 3 μM EVH2, no actin. Supernatants (S) and pellets (P) of sedimented samples were submitted to SDS-PAGE. Data are plotted as F-actin bound EVH2 versus free EVH2 as in b. The data are analyzed as in b and the curves are fit to the data using a value of the equilibrium dissociation constant of 0.69 ± 0.1 μM. (d) Competition between GST-EVH2 and VASP for binding to F-actin. F-actin (1 μM) polymerized in physiological ionic conditions was incubated with: 1, no additions; 2, 1 μM eukaryotic recombinant VASP and 4 μM GST-EVH2; 3, 4 μM GST-EVH2. Samples were sedimented at 400,000 g and supernatants (S) and pellets (P) were submitted to SDS-PAGE. A, V, and E correspond to 1 μM actin, 1 μM VASP, and 4 μM GST-EVH2, respectively. Comparison of lanes 3P and 2P shows that EVH2 is displaced from F-actin by VASP.
