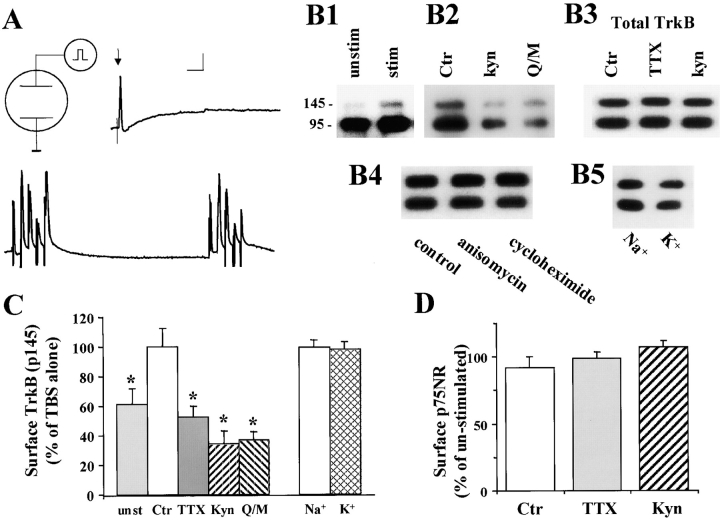
Figure 1.
Effects of TBS on BDNF receptors on neurons. Hippocampal neurons were grown in serum free medium for 11–14 d. Two platinum electrodes were positioned on opposite sides of the culture well, and the hippocampal neurons were stimulated with TBS for 60 min in a 37°C incubator in the presence or absence of various inhibitors. After electric stimulation, proteins on the surface of hippocampal neurons were biotinylated, and then examined by Western blot using antibodies against the high affinity receptor TrkB or the low affinity receptor p75. (A) Electrophysiological recording of firing patterns in cultured hippocampal neurons elicited by field electric stimulation. Top traces show that a supra-threshold field stimulation induced a single action potential. Arrow indicates application of a single field electric pulse. Scale: 20 mV and 100 ms. Bottom trace shows an example of action potentials elicited by TBS. 2 out of the 10 bursts are shown. (B) Western blot analysis of cell surface TrkB receptors. Cultures were stimulated with TBS in the presence of indicated agents as follows: TTX (1 μM); kyn (1 mM); Q/M (0.1 mM CNQX plus 80 μM MK801); anisomycin (10 μg/ml); cycloheximide (10 μg/ml); Na+ (50 mM) and K+ (50 mM). (B1) High frequency electric stimulation increases surface expression of TrkB. Both full length (145 kD) and truncated (95 kD) TrkB receptors in stimulated (stim) or unstimulated (unstim) cultures are shown. (B2) Blockade of excitatory synaptic transmission prevents the TBS-induced increase in surface TrkB. The surface TrkB was measured in cultures in the presence or absence of blockers for excitatory transmission, kyn or Q/M. (B3) The total levels of TrkB are not changed by electric stimulation. Hippocampal neurons were stimulated with TBS in the presence or absence of TTX or kyn, harvested by RIPA buffer. Total amount of TrkB were measured directly by Western blot. (B4) TBS-induced increase in surface TrkB does not require protein synthesis. Cultures were stimulated by TBS in the presence or absence of the protein synthesis inhibitor anisomycin or cycloheximide. The surface TrkB were determined by biotinylation. (B5) Simple depolarization induced by high K+ does not change the levels of surface TrkB. Biotinylation was used to determine the levels of surface TrkB in cultures that were treated with 50 mM of either control agent Na+ or the depolarizing agent K+. (C) Summary of the biotinylation experiments for surface TrkB (full length, p145). (Left) The levels of surface TrkB in TBS-stimulated cultures (set as 100%) are compared with unstimulated cultures (unst) and cultures stimulated with TBS in the presence of TTX, kyn, or Q/M; n = 7. (Right) Simple depolarization by high K+ has no effect; n = 4. The surface TrkB levels were determined in cultures that were treated with Na+ (50 mM, set as 100%) and K+ (50 mM). Asterisk indicates statistically different results (P < 0.05, ANOVA followed by post hoc tests). (D) Summary of the biotinylation experiments for surface p75NR. TTX and kyn have no effect on surface p75NR; n = 3. In this and all other bar graph figures, data from a specific experimental condition (e.g., TBS plus TTX) were normalized to the mean in control (TBS stimulation alone) groups. The results in several independent experiments (n) were pooled and averaged, and presented as mean ± SE.