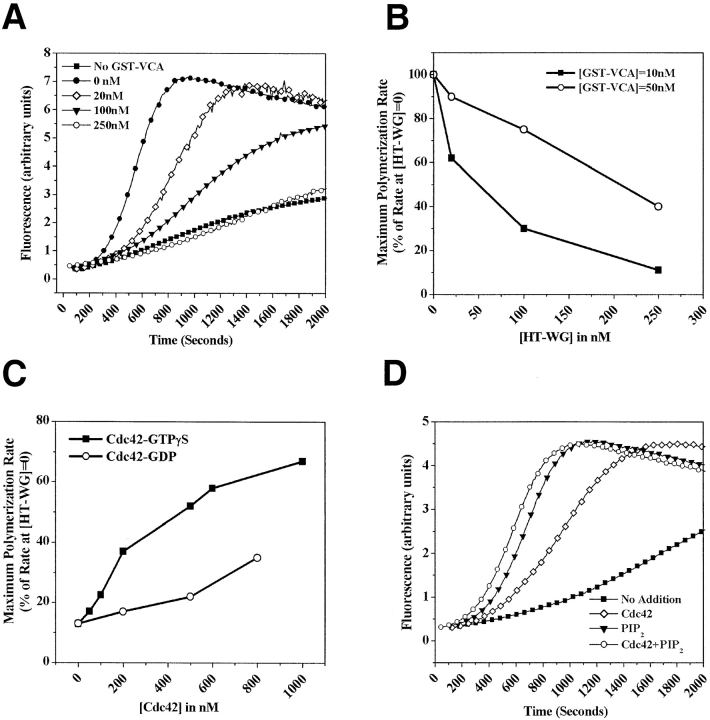
Figure 4.
The NH2-terminal domain of N-WASP inhibits Arp2/3-mediated actin nucleation activity of the VCA segment in a Cdc42, and PI(4,5)P2-regulated manner. (A) The pyrene actin assay was used to monitor the polymerization of 1.3 μM G-actin (1 μM unlabeled actin + 0.3 μM pyrene labeled actin) in the presence of Arp2/3 (30 nM), GST-VCA (10 nM), and the indicated concentrations of HT-WG. (B) The ability of GST-VCA (10 nM or 50 nM) to activate Arp2/3 complex (30 nM) was measured in the presence of increasing concentrations of HT-WG. The maximum polymerization rate, calculated from the linear phase of polymerization curves of the type shown in A, is taken as a measure of Arp2/3 activation. (C) Cdc42-GTPγS can stimulate actin polymerization (1.3 μM actin, 30 nM Arp2/3) in the presence of GST-VCA (5 nM) and HT-WG (200 nM) more effectively than Cdc42-GDP. (D) The ability of either Cdc42-GTPγS (200 nM), PI(4,5)P2-containing vesicles (10 μM), or both together to stimulate actin polymerization (1.3 μM actin, 30 nM Arp2/3 complex) in the presence of GST-VCA (5 nM) and HT-WG (200 nM).