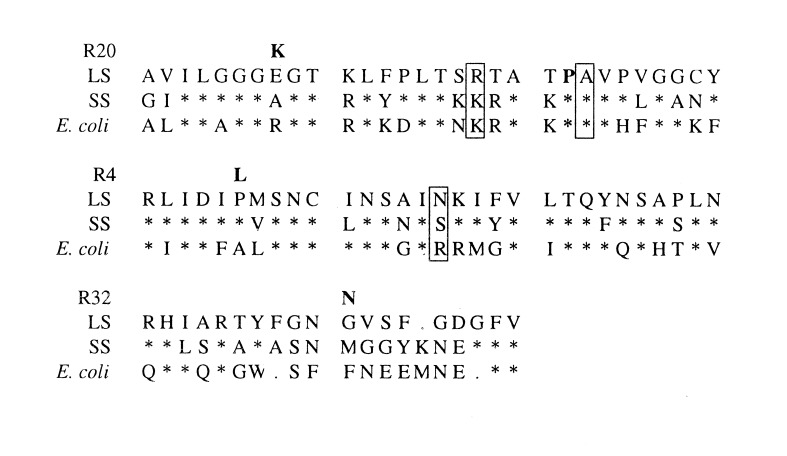
Figure 1.
Primary sequence alignments of the amino terminal sequences of potato LS, SS, and E. coli enzymes. Sequences shown begin with residue 31 for the LS, residue 21 for the SS, and residue 22 for the E. coli enzyme. Second-site mutations and their positions are indicated by the bold-faced amino acids above the residue of the LS. The P52L mutation of the potato LS that reduces the affinity for 3-PGA 45-fold and the complimentary residues on the SS and E. coli are also in bold face. Residues that alter the allosteric properties of the E. coli AGPase enzyme (26) and complimentary residues of the potato LS and SS are boxed.