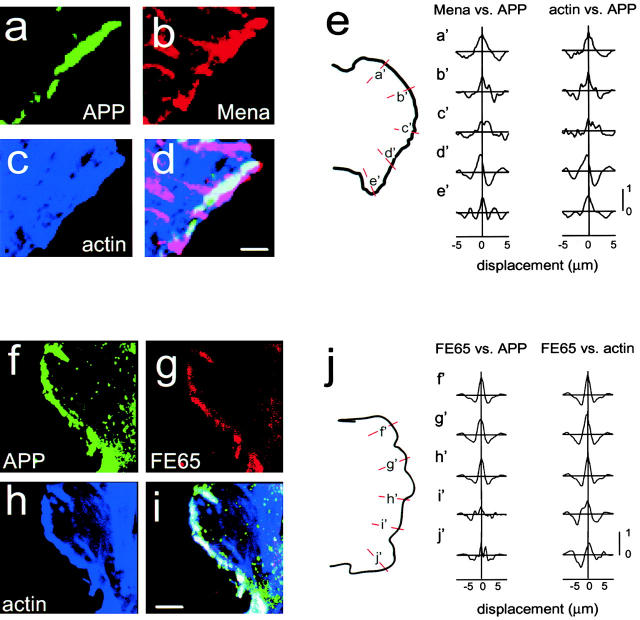
Figure 1.
APP colocalizes with FE65, Mena, and actin in lamellipodia. Lamellipodia are characterized by aggregates of actin and a dense meshwork of short actin filaments and could therefore be chosen for imaging based on their actin structure while blind to immunolabeling. Images are presented in pseudocolor. (a–d) High magnification image of H4 cells triple labeled with APP monoclonal antibodies (a), Mena polyclonal antibody (b), and Oregon green–conjugated phalloidin (c), then examined by confocal microscopy. Overlap of APP, Mena, and actin is indicated by white in the overlay (d). (f–i) High magnification image of H4 cells triple labeled with APP monoclonal antibodies (f), FE65 polyclonal antibodies (g), and Oregon green–conjugated phalloidin (h), then examined by confocal microscopy. Overlap of APP, FE65, and actin is indicated by white in the overlay (i). (e and j) Cross-covariograms from cross-correlation analysis of APP, Mena, and actin (e) and of APP, FE65, and actin (j) in lamellipodia. Lines were drawn perpendicular to the lamellipodial edge (shown in orange and labeled a′–e′ for APP, Mena, and actin and f′–j′ for APP, FE65, and actin). The intensities were determined for each line and the cross-covariograms calculated as described in Materials and Methods. All of the cross-covariograms calculated here, with the exception of c′ for both Mena and actin, have peaks >0.5, indicating significant correlation. None have a displacement greater than the half-width at half-height, indicating colocalization. Bars, 5 μm.