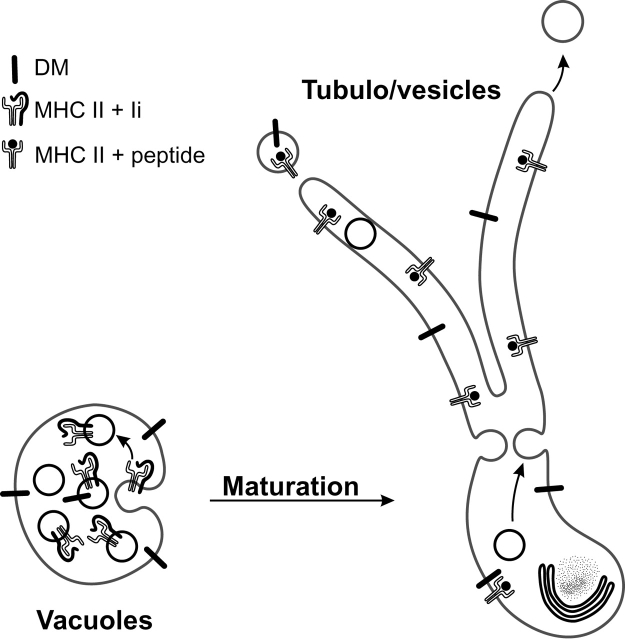
Figure 8.
Tubulation of multivesicular MIICs during DC maturation. Multivesicular MIICs in DCs undergo a dramatic shape change from vacuolar to tubular upon stimulation, most likely by fusion of the MIIC internal membrane vesicles with the limiting membrane. This implies that MHC II–rich internal membranes stored in the lumen of the vacuolar MIIC relocate to the limiting membrane of the tubular MIICs, allowing egress of MHC II from these tubules to the plasma membrane. The final transport step to the cell surface is probably mediated by transport vesicles, which bud from the tubular MIICs and nonselectively incorporate MHC II. As a consequence of MHC II translocation to the DM-rich limiting membrane, contact between DM and MHC II is increased, which may facilitate peptide loading and editing during maturation.