Figure 1.
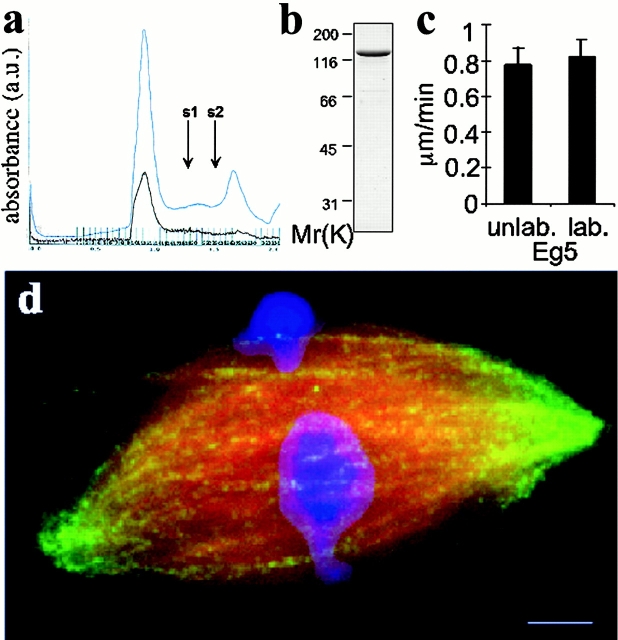
Characterization of recombinant Eg5. (a) A chromatograph for the purification by gel filtration of labeled full length Eg5 eluted from nickel charged resin. The absorbance at 280 nm (total protein, blue trace) and 590 nm (Texas red, brown trace) wavelengths of light are shown. Standards with Stokes radii 8.5 and 6.1 nm elute at volumes indicated by arrows, s1 and s2, respectively. (b) Coomassie-stained, labeled full-length Eg5 from the fraction corresponding to the major peak (13.5-nm Stokes radius) by gel filtration chromatography is resolved by SDS-PAGE. Protein from this fraction was directly used in the microscopy experiments. (c) In vitro microtubule gliding velocities of labeled and unlabeled Eg5 in 1 mM ATP. Motility assays were performed as described (Mayer et al., 1999). (d) A spindle prepared for fluorescent speckle microscopy of labeled Eg5 (green). Alexa 488–labeled tubulin and Hoechst were added to the extract to visualize the microtubules (red) and DNA (blue). Fig. 2 c shows the distribution of Eg5 alone in this spindle and Fig. 7 a provides a line scan across the image showing the distribution of Eg5 in the spindle relative to microtubules. Bar, 5 μm.