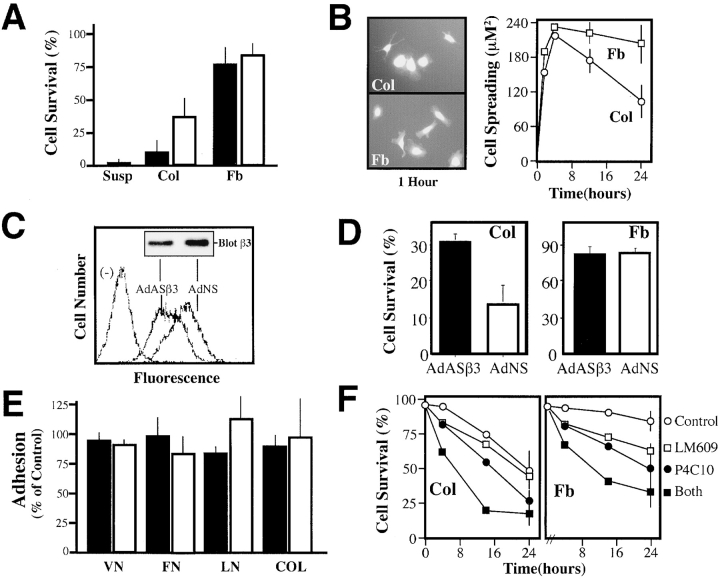
Figure 2.
Decreasing the expression of endogenous integrin αvβ3 reduces endothelial cell apoptosis during collagen culture. (A) Endothelial cells undergo apoptosis when cultured in a three-dimensional collagen matrix in the presence of complete media. HUVECs were labeled with Cell Tracker green (2 μM) and cultured in a three-dimensional collagen gel, fibrin gel, or in suspension (filled bars) or, alternatively, on the surface of collagen or fibrin gels (open bars) for 24 h. ECM-associated cells were scored for apoptosis by the morphological analysis of digital images. A representative experiment is shown, each bar is the mean survival, ± SE, of six low power fields. (B) Cell spreading was assessed in HUVECs attached to the surface of collagen (Col) or fibrin (Fb) gels (right) after capture of digital images of Cell Tracker–labeled cells (left). Cells were segmented and area calculated using IP Lab software. Data shown for each point is the mean ± SE cell area calculated at each time point from 10 low power fields. (C) The effect of treatment with a human-specific β3 integrin antisense gene, delivered by adenovirus (AdASβ3), or that of a control, nonsense adenovirus (AdNS), upon the expression of native αvβ3 in HUVECs was determined using LM609 for FACS® analysis and AP3 for immunoblotting (inset) as described in Fig. 1 A. (D) AdASβ3-treated (or AdNS-treated) HUVECs were assessed for the percentage of surviving cells after a 24 h culture in a three-dimensional collagen gel (left) or fibrin gels (right) as described above. The results shown are the mean ± SE of two fibrin or four collagen experiments. (E) β3 antisense–treated HUVECs exhibited normal levels of ECM attachment. AdASβ3-treated HUVECs (filled bars) were assessed for adhesion to wells coated with ECM components vitronectin (VN), fibronectin (FN), laminin (LN), and collagen (COL). Adhesion was quantitated by staining of attached cells with crystal violet, followed by washing, reextraction, and quantitation of the bound dye (Filardo et al., 1995), and expressed relative to untreated HUVECs. AdNS-treated HUVECs (open bars) are shown as controls. The mean ± SE of two independent experiments is shown. (F) HUVEC survival was examined in collagen (left) or fibrin (right) gels, as described above, in the presence of 30 μg/ml monoclonal antibody P4C10 (anti-β1 integrin), monoclonal antibody LM609 (anti-αvβ3 integrin), both antibodies, or control monoclonal antibody 7G7B6 (anti-CD25). Survival shown is significantly decreased at 24 h (P < 0.05) in both ECMs in the presence of P4C10 or both antibodies. One of two similar experiments is shown.