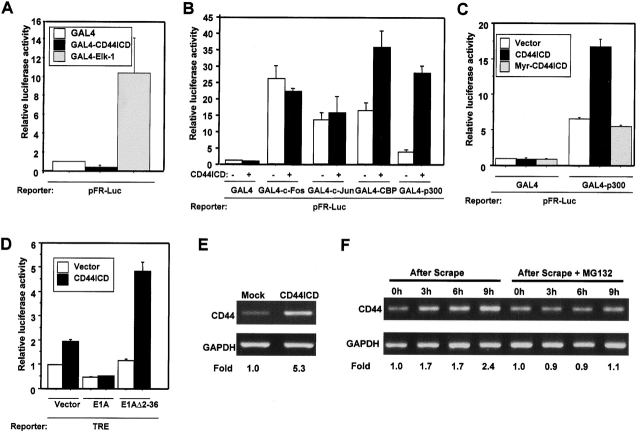
Figure 5.
Functional cooperation between CD44ICD and CBP/p300, and upregulation of CD44 transcript induced by CD44ICD. (A–C) pFR-Luc, which has five GAL4 DNA binding sites, was used as a reporter for transcription mediated by GAL4 fusion proteins. Values are relative to control cells transfected with the same amount of expression vector encoding only the GAL4 DNA-binding domain (GAL4). (A) COS-7 cells were transfected with plasmid encoding GAL4, GAL4-CD44ICD, or GAL4–Elk-1, and the transcriptional activity from the cotransfected pFR-Luc was measured. (B) COS-7 cells were cotransfected with constructs expressing indicated GAL4 fusion proteins combined with CD44ICD or the corresponding empty vector. (C) COS-7 cells were transfected with CD44ICD, Myr-CD44ICD, or the corresponding empty vector and constructs expressing GAL4-p300 or GAL4. (D) COS-7 cells were transfected with TRE reporter plasmid and CD44ICD or the corresponding empty vector. Additionally, some transfections included an expression vector encoding E1A, E1AΔ2–36 or the corresponding empty vector, as indicated. (E) HeLa cells were transfected with a plasmid encoding CD44ICD or the corresponding empty vector together with a puromycin resistance gene plasmid at a molar ratio of 20:1. The cells were fed with fresh complete medium containing puromycin (3.0 μg/ml) 24 h after transfection. 36 h after the addition of puromycin, surviving cells were serum starved for 24 h in DME/F-12 containing 0.5% FCS. Total RNA was isolated and subjected to RT-PCR analysis of the expression of CD44 mRNA. The primers used were derived from sequences in the extracellular domain of human CD44 gene (5′-ATCGATTTGAATATAACCTGCCGC-3′ and 5′-ACAATCTTCTTCAGGTGGAGCTGA-3′). The products from the RT-PCR were normalized by comparison to RT-PCR of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase mRNA. The numbers under each lane were expressed as a fold relative to control cells. (F) U251MG cells were mechanically scraped and incubated for various times as indicated in the absence or presence of MG132 (15 μM). At the indicated times, the RT-PCR analyses of the expression of CD44 mRNA were conducted as described in Fig. 4 E.