Figure 4.
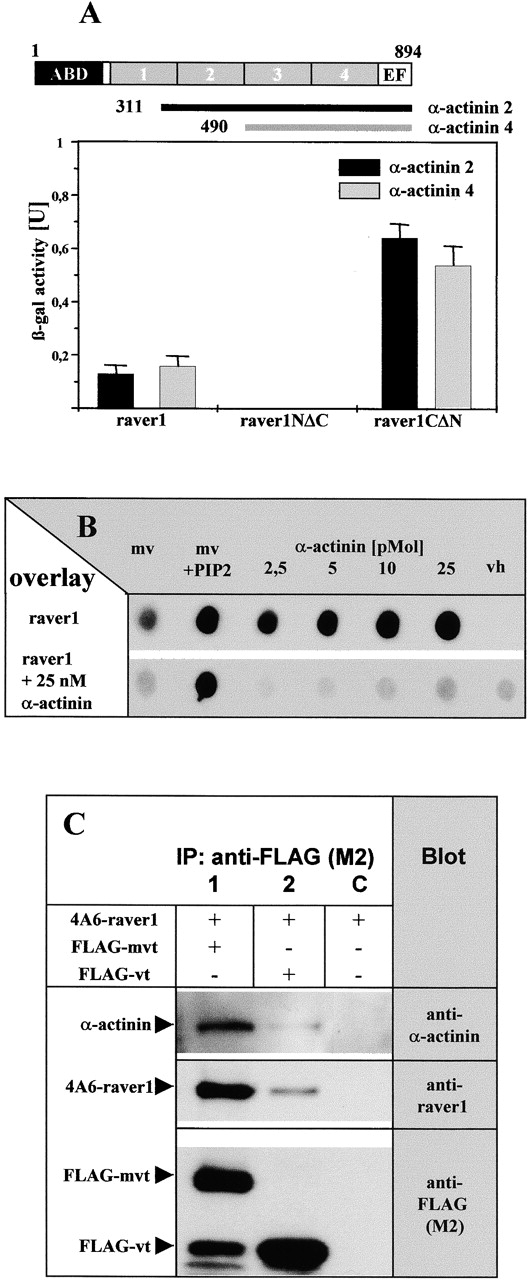
Binding to α-actinin is mediated by the COOH terminus of raver1. (A) Interaction of raver1 and its deletion fragments with COOH-terminal fragments of α-actinin 2 and 4 assayed by β-galactosidase activity in the yeast two-hybrid system. Each experiment was repeated three times, and means and SD are indicated. Organization of the α-actinin polypeptide and the fragments used are shown on top (ABD, actin binding domain; boxes 1–4, the four spectrin-like repeats; EF, EF-hand motif). (B) [35S]methionine- labeled raver1 overlay on immobilized metavinculin (mv), PIP2- activated metavinculin (mv + PIP2), α-actinin, and the vh in the presence or absence of increasing amounts of soluble α-actinin. Binding of raver1 to immobilized α-actinin is reduced significantly in the presence of soluble α-actinin. Note that binding to the vh requires the presence of α-actinin. (C) Coimmunoprecipitation of raver1 and α-actinin with vt/mvt. Bipro-tagged raver1 (4A6-raver), FLAG-mvt, or FLAG-vt were coexpressed in HeLa cells as indicated. After in situ cross-linking with DSP, immunoprecipitation (IP) with anti-FLAG (M2) was performed. Precipitates were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with the antibodies indicated. A proteolytic FLAG-tagged mvt fragment with an apparent molecular mass similar to FLAG-vt is seen in lane 1. Note that raver1 and α-actinin are coprecipitated with mvt and vt.
