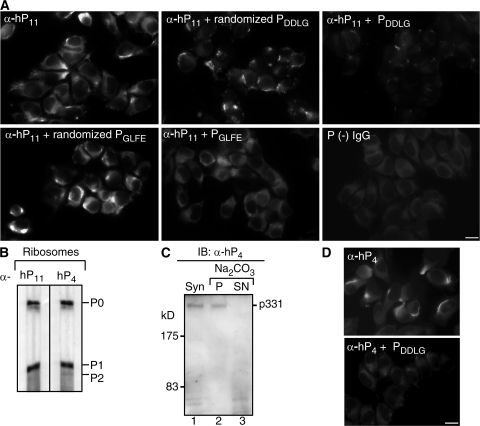
Figure 5.
Two distant regions of NSPA containing 644DDLG647 and 2881GLFD2884 sequences participate in the cell-surface interaction with anti-P autoantibodies. (A) Blocking activity of synthetic peptides against the cell-surface staining of α-hP11 antibodies involved both 644DDLG647 and 2881GLFD2884 NSPA sequences. Indirect immunofluorescence with α-hP11 in nonpermeabilized N2a cells either in the absence or presence of NSPA peptides PDDLG (642SSDDLGED649) and PGLFE (2876THMEYGLFEDV2886) or their corresponding scrambled peptides, randomized PDDLG (LGDSSEDLD) and randomized PGLFE (DEYTEHFGLVM). Both PDDLG and PGLFE peptides, but not their randomized versions, decreased the cell-surface α-hP11 immunostaining. An IgG fraction isolated from a P (−) serum gives no staining. In all of the images, some staining background is depicted on purpose to visualize the cells. Bar, 10 μm. (B–D) A subset of anti-P antibodies (α-hP4) recognize P ribosomal proteins and NSPA. A P (+) serum was subjected to affinity chromatography with the NSPA peptide DDLGEDD containing a putative P epitope (DDLG). The isolated α-hP4 antibodies, similar to the α-hP11 antibodies, recognize in immunoblot (IB) the P ribosomal proteins in ribosomes isolated from rat liver (B), and the high molecular mass protein (p331) the in synaptosomes (Syn; lane 1) and pellet (P; lane 2) but not the supernatant (SN; lane 3) of carbonate-extracted membranes (C). (D) Indirect immunofluorescence with α-hP4 antibodies shows the characteristic asymmetrical cell-surface staining, which was abrogated by the PDDLG (642SSDDLGED649) peptide. Bar, 10 μm.