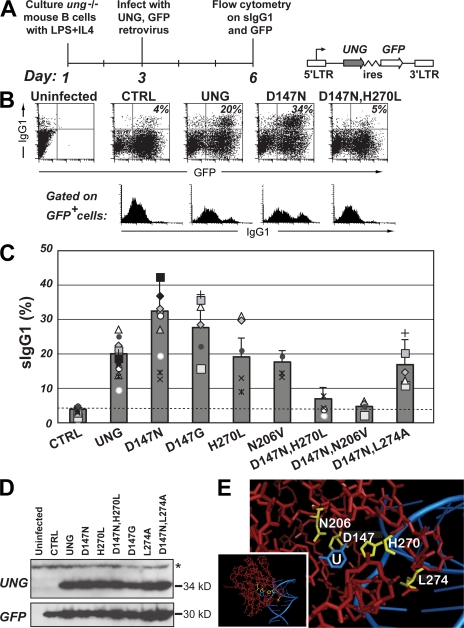
Figure 1.
Class switching in ung−/− B cells after retroviral delivery of mutant UNGs. (A) Experimental strategy with schematic representation of the retroviral vector used for UNG delivery. (B) Representative flow cytometric plots of switching to IgG1 by ung−/− B cells after retroviral delivery of mutant mouse UNGs. The proportion of retrovirally infected (GFP+-positive) cells that have switched to IgG1 is indicated in the top right quadrant of each two-dimensional plot, with the sIgG1 profile of the gated GFP+ cells shown below. (C) Compilation of the results of multiple comparisons of switching to IgG1 achieved with different mutant mouse UNGs. The histogram presents the results of 13 independent experiments represented by the different symbols (each using B cells prepared from a single mouse), with each mutant being analyzed in at least 4 separate experiments. To facilitate comparison of the results obtained in different experiments, a common symbol is used to depict the results obtained in a single experimental set. To facilitate comparison of overall switching proficiency of the different UNG mutants, as deduced from multiple experiments, the means in the histograms are presented as values plus the SD that were normalized to 20% switching by wild-type UNG. The switching achieved using the D147N, D147G, (D147N,H270L), and (D147N,N206V) mutants differs significantly from that achieved with wild-type UNG (P < 0.05 for the single mutants; P < 0.001 for the double mutants). (D) Expression of the different UNG mutants analyzed by Western blot of extracts from the retroviral packaging cells. A Western blot for GFP provides a control. The N206V mutation prevents recognition by the anti-UNG antibody, although the UNG-N206V mutant yields uracil-excision activity and supports switch recombination (C and Fig. 3 C). A nonspecific band recognized by the anti-UNG antibody is indicated by an asterisk. (E) The amino acid positions mutagenized in mouse UNG (yellow) are highlighted on a structure of human UNG (red) cocrystallized with a U-containing DNA fragment (blue; pdb 1SSP [36]) in which U is flipped out of the DNA helix and into the enzyme active site. The area surrounding the active site has been zoomed in from the whole structure (inset). Residue numbering is as in mouse UNG nuclear isoform.