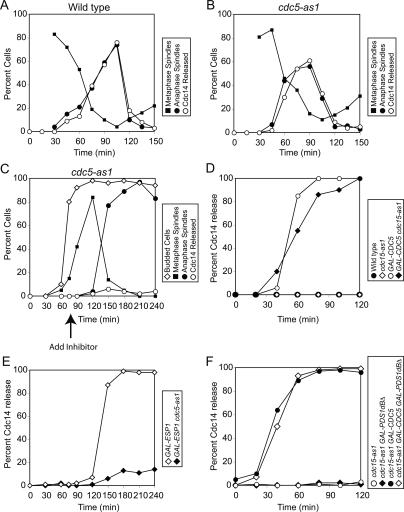
Figure 4.
Cdc5’s role in promoting Cdc14 release is restricted to metaphase and anaphase. (A,B) Wild-type (A1411; A) and cdc5-as1 (cdc5L158G; Ry1260; B) cells carrying a CDC14-3HA fusion were arrested in G1 in YEPD with α-factor pheromone (5 μg/mL). After 3 h, cells were released into medium lacking pheromone but containing nocodazole (15 μg/mL) and the CMK inhibitor (5 μM). When the arrest was complete, cells were released into YEPD supplemented with 1% DMSO. The percentage of cells with metaphase spindles (closed squares) and anaphase spindles (closed circles), as well as the percentage of cells with Cdc14-HA released from the nucleolus (open circles), was determined at the indicated times. Note: Spindle morphology was not analyzed 0 and 15 min after release from the nocodazole block because the spindle had not yet reformed. (C) cdc5-as1 GAL-ESP1 CDC14-3HA (Ry1287) cells were arrested in G1 in YEP + 2% Raffinose (YEPR) with α-factor pheromone (5 μg/mL). Two-and-a-half hours into the arrest, 2% galactose (YEPR + G) was added to induce GAL-ESP1 expression. When the arrest was complete (3 h total), cells were released into YEPR + G lacking the pheromone. Seventy-five minutes after the release, when ∼80% of cells had formed a bud and were about to enter metaphase, CMK inhibitor (5 μM) was added. The percentage of budded cells (open diamonds), cells with metaphase spindles (closed squares) and anaphase spindles (closed circles), and the percentage of cells with Cdc14-HA released from the nucleolus (open circles) was determined at the indicated times. (D) Wild-type (A1411; closed circles), cdc15-as1 (A11617; open diamonds), GAL-CDC5 (A3317; open circles), and cdc15-as1 GAL-CDC5 (Ry1245; closed diamonds) cells carrying CDC14-3HA were arrested in G1 in YEP supplemented with 2% Raffinose (YEPR) with α-factor pheromone (5 μg/ mL). After 3 h, cells were released into medium lacking pheromone but supplemented with hydroxyurea (10 mg/mL) and the cdc15-as1 inhibitor (5 μM). After 2.5 h, when cells had arrested in S phase, 2% galactose was added to induce the expression of CDC5 from the inducible GAL1-10 promoter. The percentage of cells with Cdc14-HA released from the nucleolus was determined at the indicated times. (E) GAL-ESP1 (A4150) and cdc5-as1 GAL-ESP1 (Ry1287) cells carrying a CDC14-3HA fusion were treated as described in Figure 6C, except that cells were released into YEPR + G lacking pheromone but supplemented with 15 μg/mL nocodazole. (F) cdc15-as1 (Ry1386; open circles), cdc15-as1 GAL-PDS1dBΔ (Ry1385; closed diamonds), cdc15-as1 GAL-CDC5 (Ry1384; closed circles), and cdc15-as1 GAL-PDS1dBΔ GAL-CDC5 (Ry1383; open diamonds) cells were arrested with hydroxyurea (10 mg/mL). When the arrest was complete, the cdc15-as1 inhibitor (5 μM) was added. One hour after the inhibitor addition, 2% galactose was added to induce the expression of CDC5 and PDS1dBΔ from the inducible GAL1-10 promoter. The percentage of cells with Cdc14-HA released from the nucleolus was determined at the indicated times.